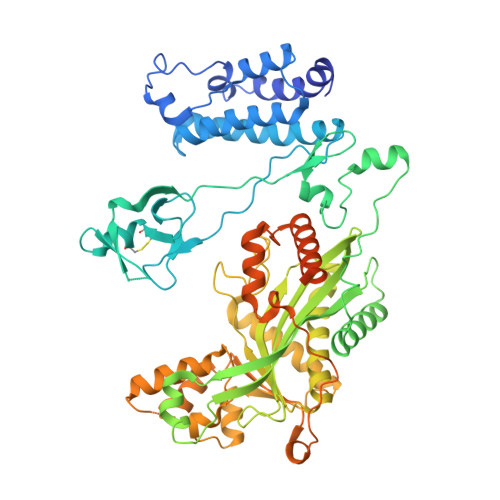
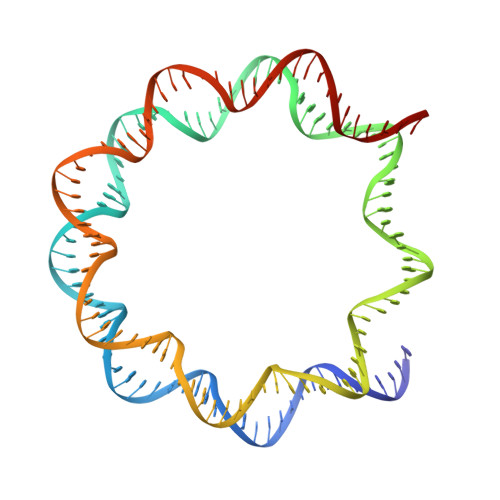
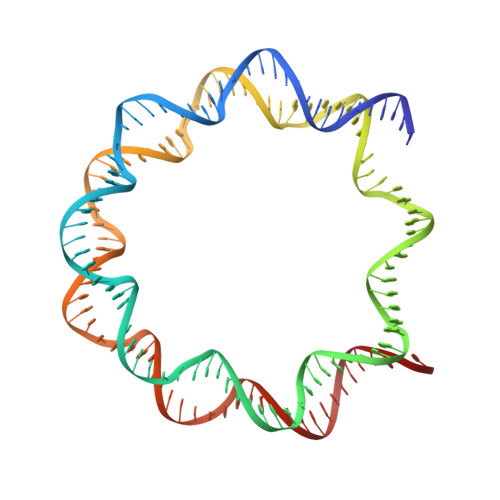
Structural basis for binding diversity of acetyltransferase p300 to the nucleosome.
Hatazawa, S., Liu, J., Takizawa, Y., Zandian, M., Negishi, L., Kutateladze, T.G., Kurumizaka, H.(2022) iScience 25: 104563-104563
- PubMed: 35754730
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.104563
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W9V - PubMed Abstract:
p300 is a human acetyltransferase that associates with chromatin and mediates vital cellular processes. We now report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the p300 catalytic core in complex with the nucleosome core particle (NCP). In the most resolved structure, the HAT domain and bromodomain of p300 contact nucleosomal DNA at superhelical locations 2 and 3, and the catalytic site of the HAT domain are positioned near the N-terminal tail of histone H4. Mutations of the p300-DNA interfacial residues of p300 substantially decrease binding to NCP. Three additional classes of p300-NCP complexes show different modes of the p300-NCP complex formation. Our data provide structural details critical to our understanding of the mechanism by which p300 acetylates multiple sites on the nucleosome.
- Laboratory of Chromatin Structure and Function, Institute for Quantitative Biosciences, The University of Tokyo, 1-1-1 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: