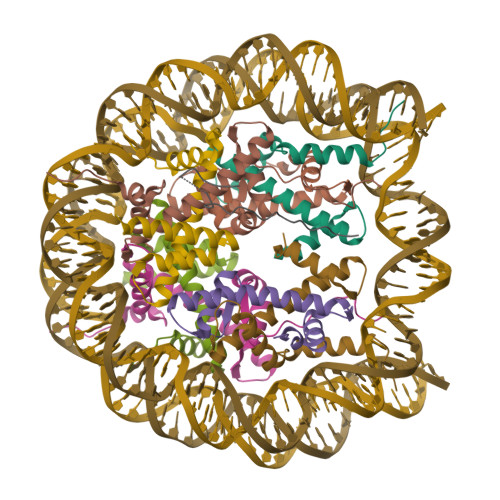
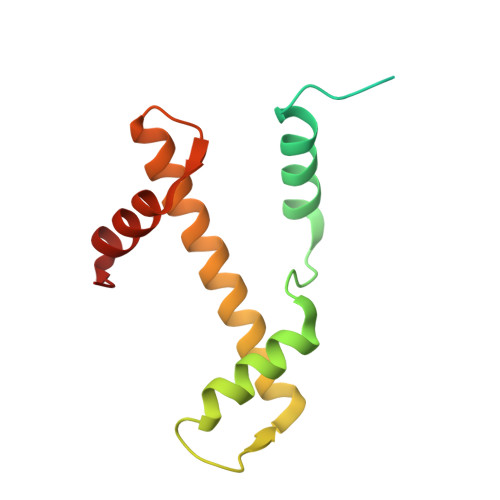
The N-terminal region of DNMT3A engages the nucleosome surface to aid chromatin recruitment.
Wapenaar, H., Clifford, G., Rolls, W., Pasquier, M., Burdett, H., Zhang, Y., Deak, G., Zou, J., Spanos, C., Taylor, M.R.D., Mills, J., Watson, J.A., Kumar, D., Clark, R., Das, A., Valsakumar, D., Bramham, J., Voigt, P., Sproul, D., Wilson, M.D.(2024) EMBO Rep 25: 5743-5779
- PubMed: 39528729
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44319-024-00306-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QZM - PubMed Abstract:
DNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) plays a critical role in establishing and maintaining DNA methylation patterns in vertebrates. Here we structurally and biochemically explore the interaction of DNMT3A1 with diverse modified nucleosomes indicative of different chromatin environments. A cryo-EM structure of the full-length DNMT3A1-DNMT3L complex with a H2AK119ub nucleosome reveals that the DNMT3A1 ubiquitin-dependent recruitment (UDR) motif interacts specifically with H2AK119ub and makes extensive contacts with the core nucleosome histone surface. This interaction facilitates robust DNMT3A1 binding to nucleosomes, and previously unexplained DNMT3A disease-associated mutations disrupt this interface. Furthermore, the UDR-nucleosome interaction synergises with other DNMT3A chromatin reading elements in the absence of histone ubiquitylation. H2AK119ub does not stimulate DNMT3A DNA methylation activity, as observed for the previously described H3K36me2 mark, which may explain low levels of DNA methylation on H2AK119ub marked facultative heterochromatin. This study highlights the importance of multivalent binding of DNMT3A to histone modifications and the nucleosome surface and increases our understanding of how DNMT3A1 chromatin recruitment occurs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Wellcome Centre for Cell Biology, University of Edinburgh, Michael Swann Building, Kings Buildings, Mayfield Road, Edinburgh, EH9 3JR, UK.