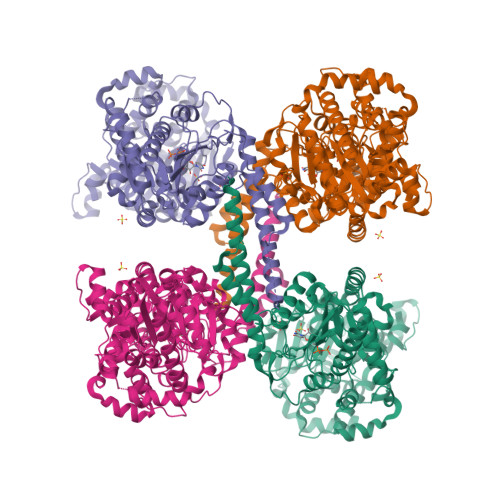
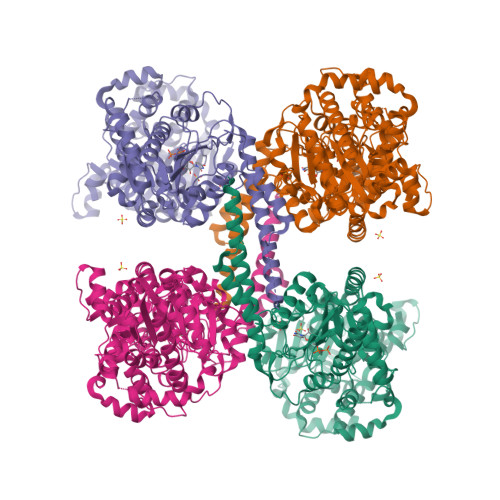
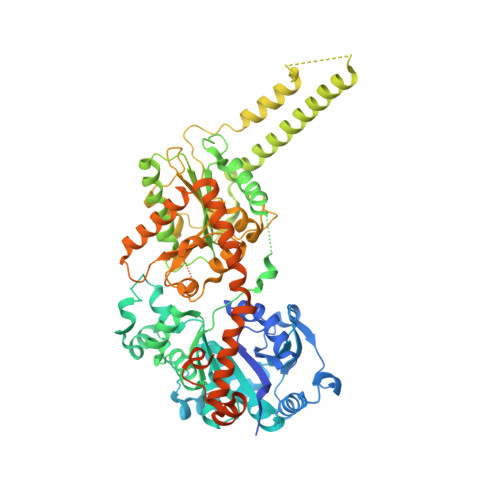
Structural basis for glucose-6-phosphate activation of glycogen synthase.
Baskaran, S., Roach, P.J., Depaoli-Roach, A.A., Hurley, T.D.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 17563-17568
- PubMed: 20876143
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006340107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3NAZ, 3NB0, 3NCH, 3O3C - PubMed Abstract:
Regulation of the storage of glycogen, one of the major energy reserves, is of utmost metabolic importance. In eukaryotes, this regulation is accomplished through glucose-6-phosphate levels and protein phosphorylation. Glycogen synthase homologs in bacteria and archaea lack regulation, while the eukaryotic enzymes are inhibited by protein kinase mediated phosphorylation and activated by protein phosphatases and glucose-6-phosphate binding. We determined the crystal structures corresponding to the basal activity state and glucose-6-phosphate activated state of yeast glycogen synthase-2. The enzyme is assembled into an unusual tetramer by an insertion unique to the eukaryotic enzymes, and this subunit interface is rearranged by the binding of glucose-6-phosphate, which frees the active site cleft and facilitates catalysis. Using both mutagenesis and intein-mediated phospho-peptide ligation experiments, we demonstrate that the enzyme's response to glucose-6-phosphate is controlled by Arg583 and Arg587, while four additional arginine residues present within the same regulatory helix regulate the response to phosphorylation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molelcular Biology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202-5122, USA.