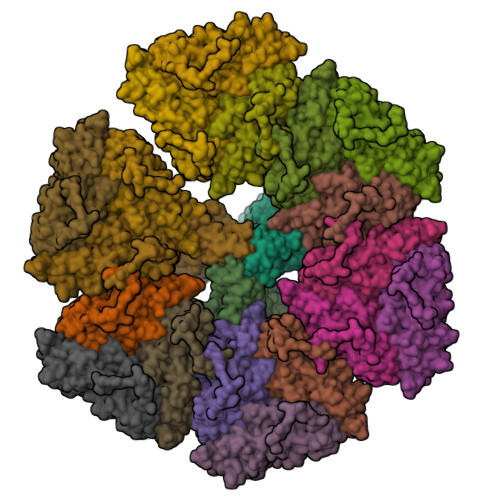
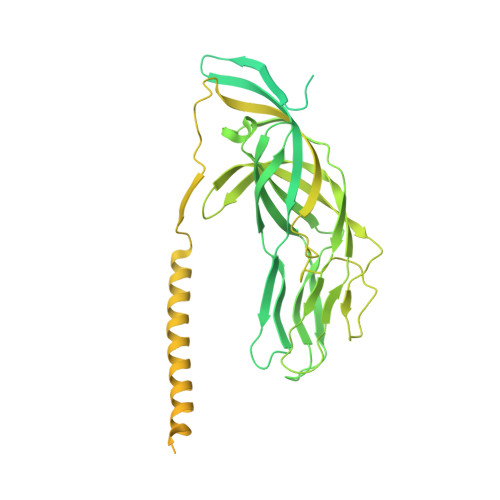
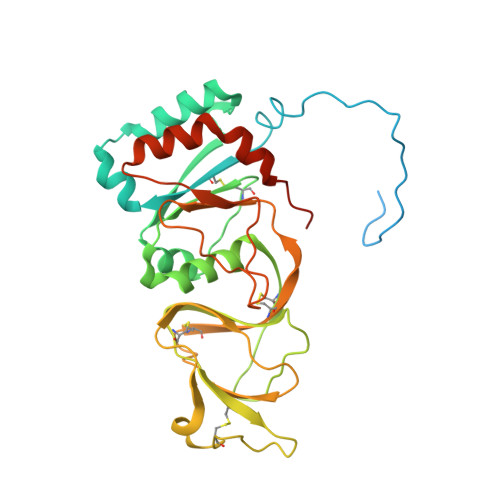
The rotavirus VP5*/VP8* conformational transition permeabilizes membranes to Ca2.
de Sautu, M., Herrmann, T., Scanavachi, G., Jenni, S., Harrison, S.C.(2024) PLoS Pathog 20: e1011750-e1011750
- PubMed: 38574119
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1011750
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8UK2, 8UK3 - PubMed Abstract:
Rotaviruses infect cells by delivering into the cytosol a transcriptionally active inner capsid particle (a "double-layer particle": DLP). Delivery is the function of a third, outer layer, which drives uptake from the cell surface into small vesicles from which the DLPs escape. In published work, we followed stages of rhesus rotavirus (RRV) entry by live-cell imaging and correlated them with structures from cryogenic electron microscopy and tomography (cryo-EM and cryo-ET). The virus appears to wrap itself in membrane, leading to complete engulfment and loss of Ca2+ from the vesicle produced by the wrapping. One of the outer-layer proteins, VP7, is a Ca2+-stabilized trimer; loss of Ca2+ releases both VP7 and the other outer-layer protein, VP4, from the particle. VP4, activated by cleavage into VP8* and VP5*, is a trimer that undergoes a large-scale conformational rearrangement, reminiscent of the transition that viral fusion proteins undergo to penetrate a membrane. The rearrangement of VP5* thrusts a 250-residue, C-terminal segment of each of the three subunits outward, while allowing the protein to remain attached to the virus particle and to the cell being infected. We proposed that this segment inserts into the membrane of the target cell, enabling Ca2+ to cross. In the work reported here, we show the validity of key aspects of this proposed sequence. By cryo-EM studies of liposome-attached virions ("triple-layer particles": TLPs) and single-particle fluorescence imaging of liposome-attached TLPs, we confirm insertion of the VP4 C-terminal segment into the membrane and ensuing generation of a Ca2+ "leak". The results allow us to formulate a molecular description of early events in entry. We also discuss our observations in the context of other work on double-strand RNA virus entry.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America.