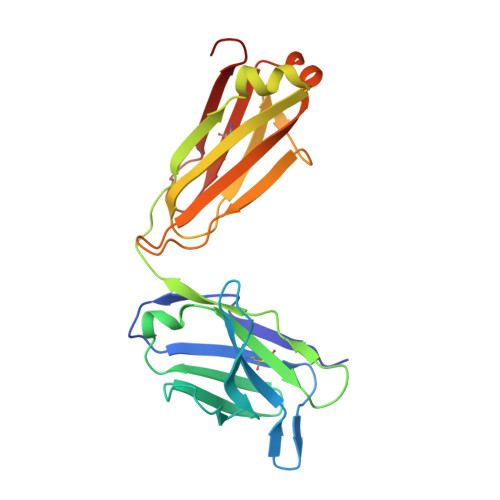
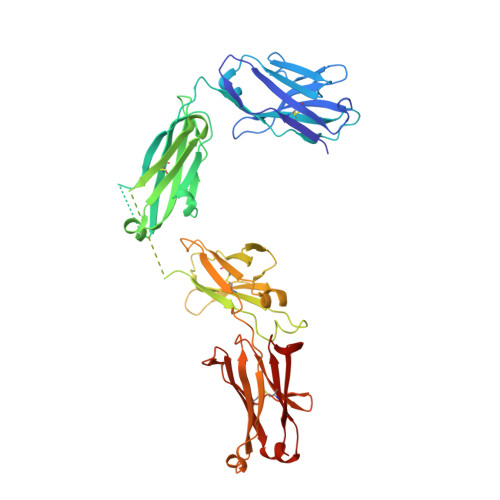
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering as a Powerful Tool for Phase and Crystallinity Assessment of Monoclonal Antibody Crystallites in Support of Batch Crystallization.
Larpent, P., Codan, L., Bothe, J.R., Iuzzolino, L., Pabit, S., Gupta, S., Fischmann, T., Su, Y., Reichert, P., Stueber, D., Cote, A.(2024) Mol Pharm
- PubMed: 38958508
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00418
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SJK - PubMed Abstract:
Crystalline suspensions of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have great potential to improve drug substance isolation and purification on a large scale and to be used for drug delivery via high-concentration formulations. Crystalline mAb suspensions are expected to have enhanced chemical and physical properties relative to mAb solutions delivered intravenously, making them attractive candidates for subcutaneous delivery. In contrast to small molecules, the development of protein crystalline suspensions is not a widely used approach in the pharmaceutical industry. This is mainly due to the challenges in finding crystalline hits and the suboptimal physical properties of the resulting crystallites when hits are found. Modern advances in instrumentation and increased knowledge of mAb crystallization have, however, resulted in higher probabilities of discovering crystal forms and improving their particle properties and characterization. In this regard, physical, analytical characterization plays a central role in the initial steps of understanding and later optimizing the crystallization of mAbs and requires careful selection of the appropriate tools. This contribution describes a novel crystal structure of the antibody pembrolizumab and demonstrates the usefulness of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) for characterizing its crystalline suspensions. It illustrates the advantages of SAXS when used to (i) confirm crystallinity and crystal phase of crystallites produced in batch mode; (ii) confirm crystallinity under various conditions and detect variations in crystal phases, enabling fine-tuning of the crystallizations for phase control across multiple batches; (iii) monitor the physical response and stability of the crystallites in suspension with regard to filtration and washing; and (iv) monitor the physical stability of the crystallites upon drying. Overall, this work highlights how SAXS is an essential tool for mAb crystallization characterization.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Analytical Research and Development, MSD Werthenstein BioPharma GmbH, Industrie Nord 1, 6105 Schachen, Switzerland.