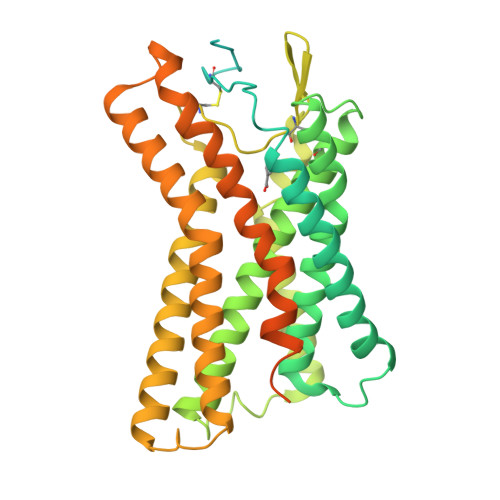
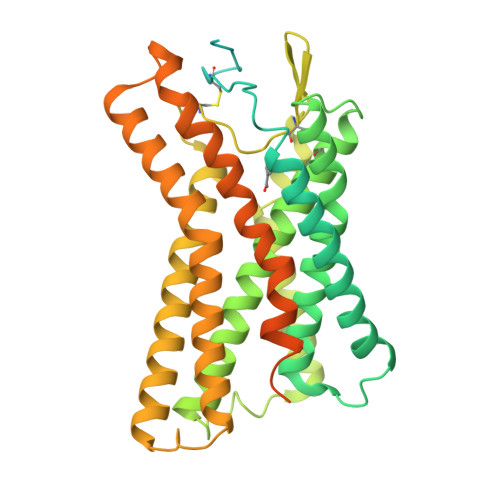
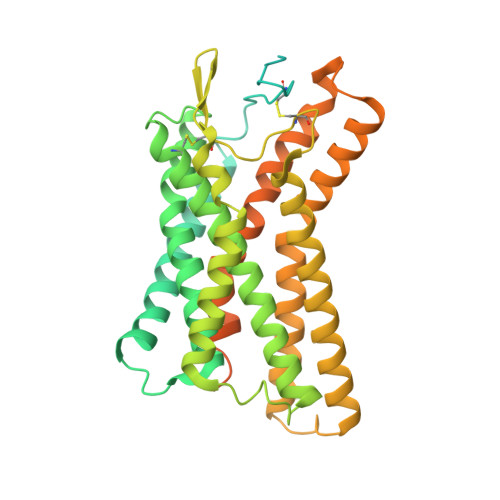
Structural basis for ligand recognition and signaling of hydroxy-carboxylic acid receptor 2.
Park, J.H., Kawakami, K., Ishimoto, N., Ikuta, T., Ohki, M., Ekimoto, T., Ikeguchi, M., Lee, D.S., Lee, Y.H., Tame, J.R.H., Inoue, A., Park, S.Y.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 7150-7150
- PubMed: 37932263
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-42764-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8I7V, 8I7W, 8K5B, 8K5C, 8K5D - PubMed Abstract:
Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors (HCAR1, HCAR2, and HCAR3) transduce G i/o signaling upon biding to molecules such as lactic acid, butyric acid and 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid, which are associated with lipolytic and atherogenic activity, and neuroinflammation. Although many reports have elucidated the function of HCAR2 and its potential as a therapeutic target for treating not only dyslipidemia but also neuroimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease, the structural basis of ligand recognition and ligand-induced G i -coupling remains unclear. Here we report three cryo-EM structures of the human HCAR2-G i signaling complex, each bound with different ligands: niacin, acipimox or GSK256073. All three agonists are held in a deep pocket lined by residues that are not conserved in HCAR1 and HCAR3. A distinct hairpin loop at the HCAR2 N-terminus and extra-cellular loop 2 (ECL2) completely enclose the ligand. These structures also reveal the agonist-induced conformational changes propagated to the G-protein-coupling interface during activation. Collectively, the structures presented here are expected to help in the design of ligands specific for HCAR2, leading to new drugs for the treatment of various diseases such as dyslipidemia and inflammation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Drug Design Laboratory, Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, Tsurumi, Yokohama, 230-0045, Japan.