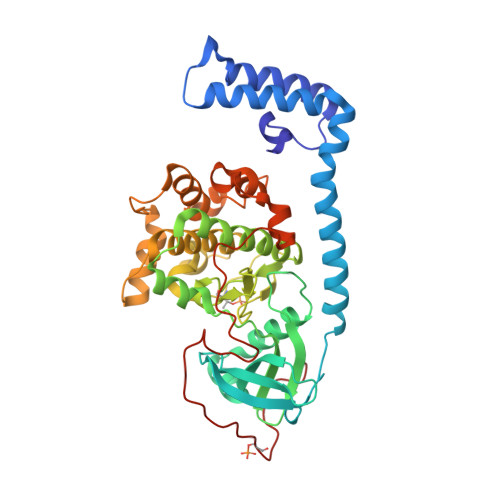
Discovery and Synthesis of a Naturally Derived Protein Kinase Inhibitor that Selectively Inhibits Distinct Classes of Serine/Threonine Kinases.
Du, L., Wilson, B.A.P., Li, N., Shah, R., Dalilian, M., Wang, D., Smith, E.A., Wamiru, A., Goncharova, E.I., Zhang, P., O'Keefe, B.R.(2023) J Nat Prod 86: 2283-2293
- PubMed: 37843072
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00394
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FE2, 8FE5, 8FEC - PubMed Abstract:
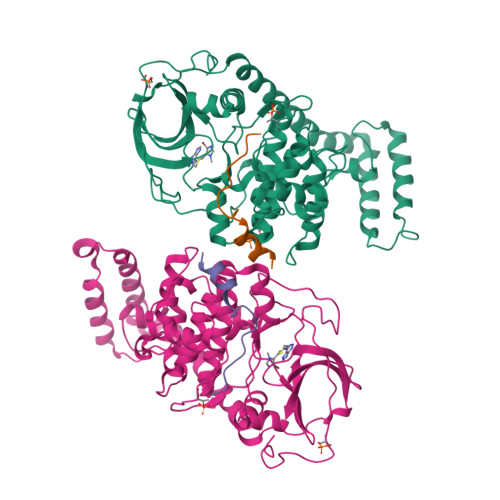
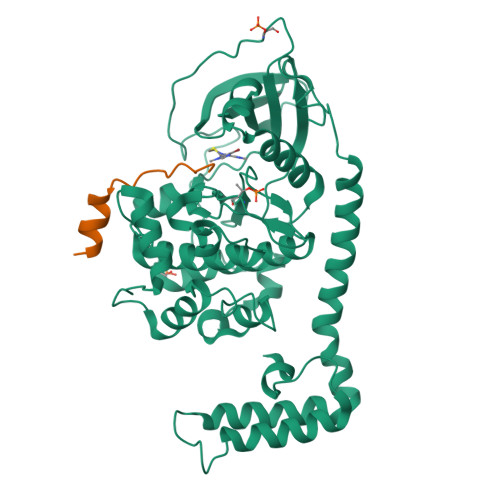
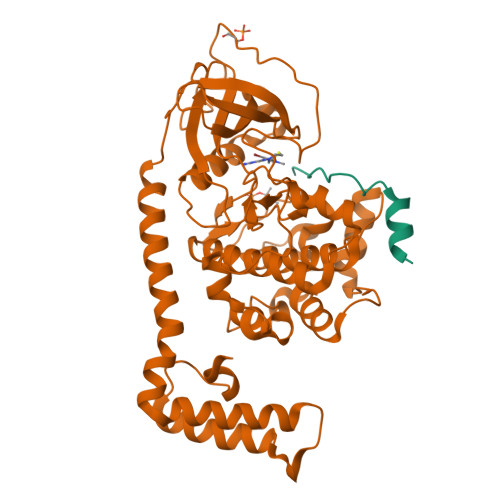
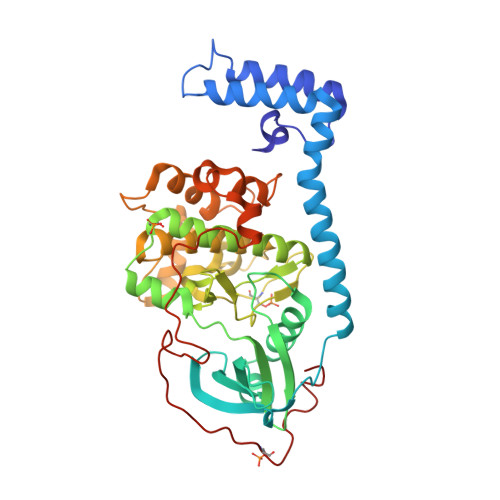
The DNAJB1-PRKACA oncogenic gene fusion results in an active kinase enzyme, J-PKAcα, that has been identified as an attractive antitumor target for fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLHCC). A high-throughput assay was used to identify inhibitors of J-PKAcα catalytic activity by screening the NCI Program for Natural Product Discovery (NPNPD) prefractionated natural product library. Purification of the active agent from a single fraction of an Aplidium sp. marine tunicate led to the discovery of two unprecedented alkaloids, aplithianines A ( 1 ) and B ( 2 ). Aplithianine A ( 1 ) showed potent inhibition against J-PKAcα with an IC 50 of ∼1 μM in the primary screening assay. In kinome screening, 1 inhibited wild-type PKA with an IC 50 of 84 nM. Further mechanistic studies including cocrystallization and X-ray diffraction experiments revealed that 1 inhibited PKAcα catalytic activity by competitively binding to the ATP pocket. Human kinome profiling of 1 against a panel of 370 kinases revealed potent inhibition of select serine/threonine kinases in the CLK and PKG families with IC 50 values in the range ∼11-90 nM. An efficient, four-step total synthesis of 1 has been accomplished, enabling further evaluation of aplithianines as biologically relevant kinase inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Targets Program, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, Frederick, Maryland 21702, United States.