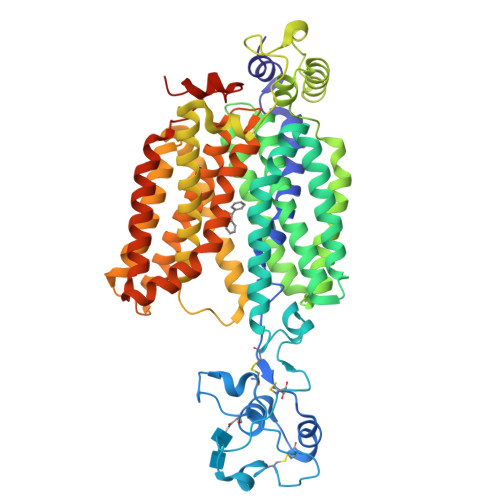
Molecular basis of polyspecific drug and xenobiotic recognition by OCT1 and OCT2.
Suo, Y., Wright, N.J., Guterres, H., Fedor, J.G., Butay, K.J., Borgnia, M.J., Im, W., Lee, S.Y.(2023) Nat Struct Mol Biol 30: 1001-1011
- PubMed: 37291422
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-023-01017-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ET6, 8ET7, 8ET8, 8ET9 - PubMed Abstract:
A wide range of endogenous and xenobiotic organic ions require facilitated transport systems to cross the plasma membrane for their disposition. In mammals, organic cation transporter (OCT) subtypes 1 and 2 (OCT1 and OCT2, also known as SLC22A1 and SLC22A2, respectively) are polyspecific transporters responsible for the uptake and clearance of structurally diverse cationic compounds in the liver and kidneys, respectively. Notably, it is well established that human OCT1 and OCT2 play central roles in the pharmacokinetics and drug-drug interactions of many prescription medications, including metformin. Despite their importance, the basis of polyspecific cationic drug recognition and the alternating access mechanism for OCTs have remained a mystery. Here we present four cryo-electron microscopy structures of apo, substrate-bound and drug-bound OCT1 and OCT2 consensus variants, in outward-facing and outward-occluded states. Together with functional experiments, in silico docking and molecular dynamics simulations, these structures uncover general principles of organic cation recognition by OCTs and provide insights into extracellular gate occlusion. Our findings set the stage for a comprehensive structure-based understanding of OCT-mediated drug-drug interactions, which will prove critical in the preclinical evaluation of emerging therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, USA.