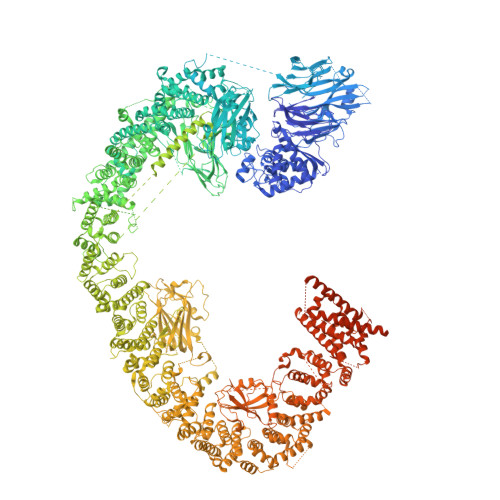
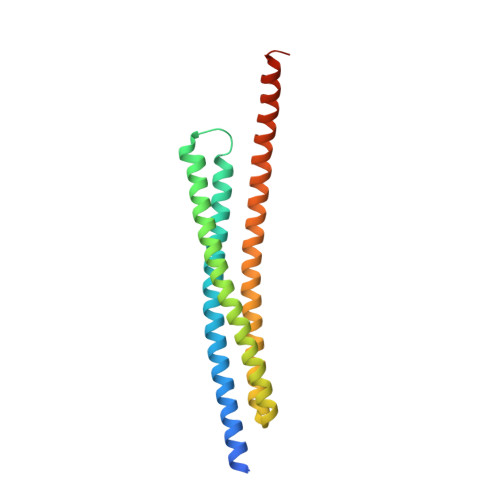
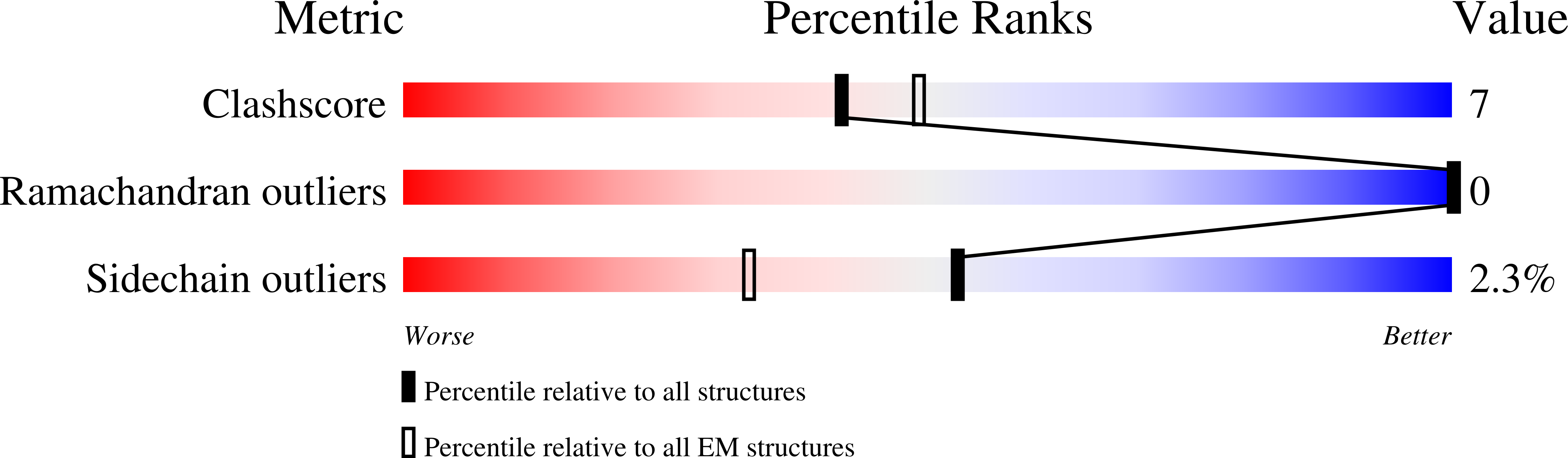Structures of BIRC6-client complexes provide a mechanism of SMAC-mediated release of caspases.
Hunkeler, M., Jin, C.Y., Fischer, E.S.(2023) Science 379: 1105-1111
- PubMed: 36758104
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.ade5750
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8E2D, 8E2E, 8E2F, 8E2G, 8E2H, 8E2I, 8E2J, 8E2K - PubMed Abstract:
Tight regulation of apoptosis is essential for metazoan development and prevents diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration. Caspase activation is central to apoptosis, and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) are the principal actors that restrain caspase activity and are therefore attractive therapeutic targets. IAPs, in turn, are regulated by mitochondria-derived proapoptotic factors such as SMAC and HTRA2. Through a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length human baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 6 (BIRC6) bound to SMAC, caspases, and HTRA2, we provide a molecular understanding for BIRC6-mediated caspase inhibition and its release by SMAC. The architecture of BIRC6, together with near-irreversible binding of SMAC, elucidates how the IAP inhibitor SMAC can effectively control a processive ubiquitin ligase to respond to apoptotic stimuli.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cancer Biology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA 02215, USA.