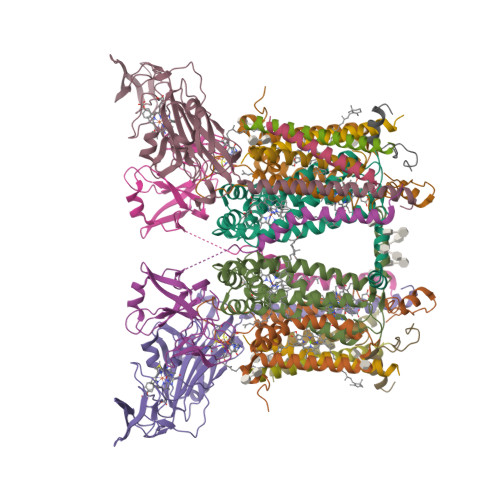
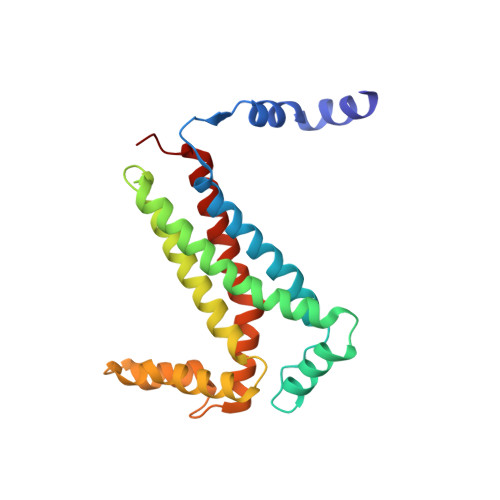
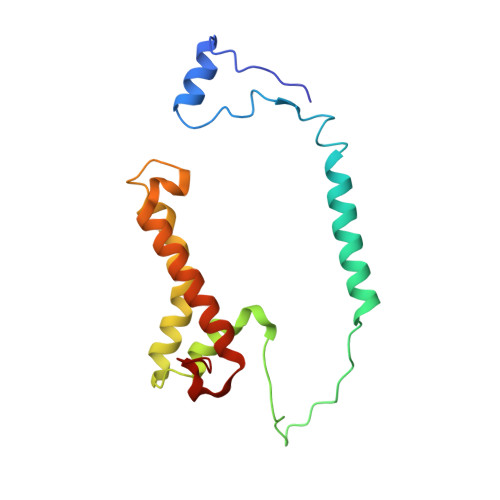
High-resolution cryo-EM structures of plant cytochrome b 6 f at work.
Sarewicz, M., Szwalec, M., Pintscher, S., Indyka, P., Rawski, M., Pietras, R., Mielecki, B., Koziej, L., Jaciuk, M., Glatt, S., Osyczka, A.(2023) Sci Adv 9: eadd9688-eadd9688
- PubMed: 36638176
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.add9688
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QRM, 7ZYV - PubMed Abstract:
Plants use solar energy to power cellular metabolism. The oxidation of plastoquinol and reduction of plastocyanin by cytochrome b 6 f (Cyt b 6 f) is known as one of the key steps of photosynthesis, but the catalytic mechanism in the plastoquinone oxidation site (Q p ) remains elusive. Here, we describe two high-resolution cryo-EM structures of the spinach Cyt b 6 f homodimer with endogenous plastoquinones and in complex with plastocyanin. Three plastoquinones are visible and line up one after another head to tail near Q p in both monomers, indicating the existence of a channel in each monomer. Therefore, quinones appear to flow through Cyt b 6 f in one direction, transiently exposing the redox-active ring of quinone during catalysis. Our work proposes an unprecedented one-way traffic model that explains efficient quinol oxidation during photosynthesis and respiration.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics, and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland.