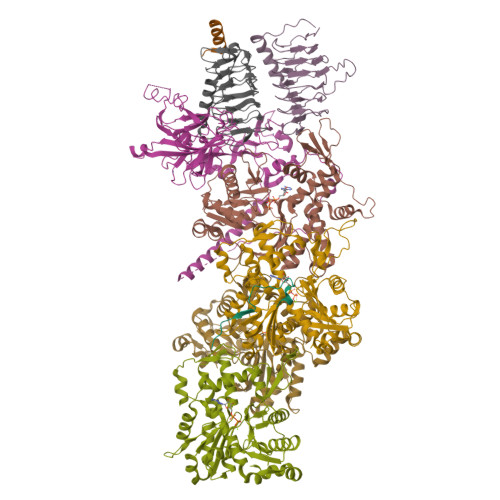
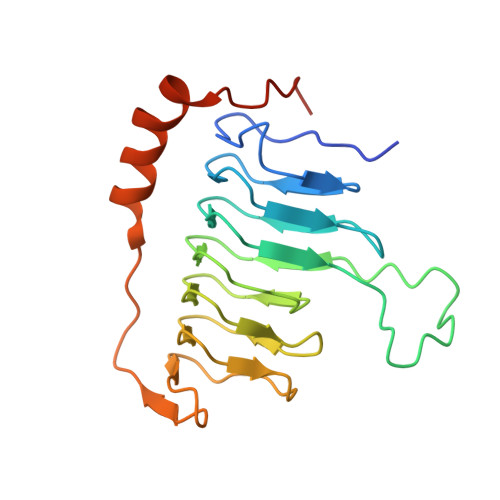
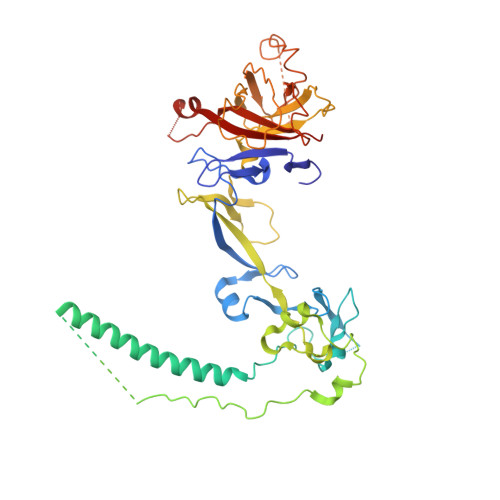
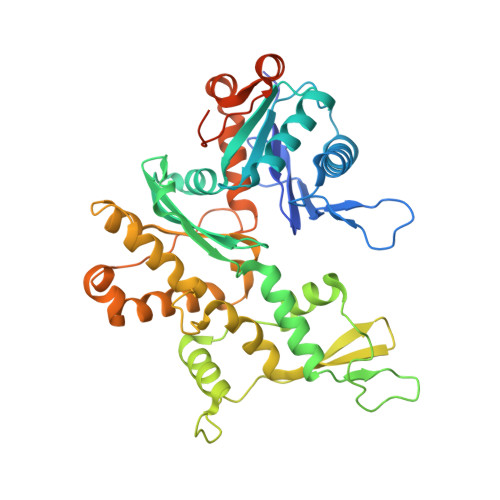
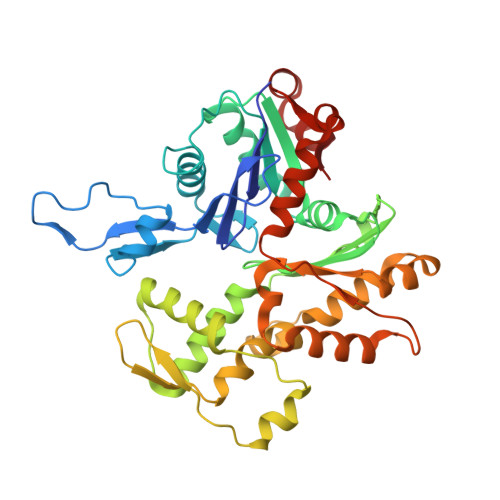
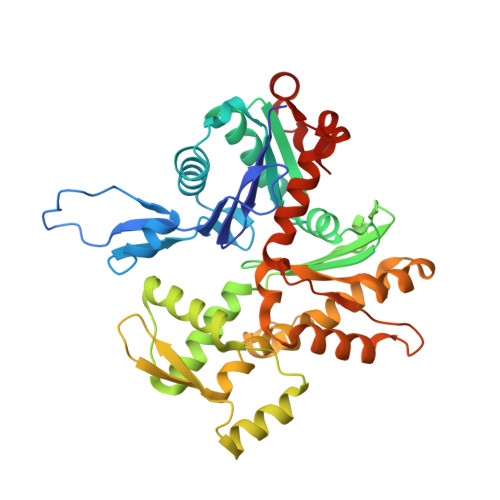
Structure of dynein-dynactin on microtubules shows tandem adaptor binding.
Chaaban, S., Carter, A.P.(2022) Nature 610: 212-216
- PubMed: 36071160
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05186-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Z8F, 7Z8G, 7Z8H, 7Z8I, 7Z8J, 7Z8K, 7Z8L, 7Z8M - PubMed Abstract:
Cytoplasmic dynein is a microtubule motor that is activated by its cofactor dynactin and a coiled-coil cargo adaptor 1-3 . Up to two dynein dimers can be recruited per dynactin, and interactions between them affect their combined motile behaviour 4-6 . Different coiled-coil adaptors are linked to different cargos 7,8 , and some share motifs known to contact sites on dynein and dynactin 4,9-13 . There is limited structural information on how the resulting complex interacts with microtubules and how adaptors are recruited. Here we develop a cryo-electron microscopy processing pipeline to solve the high-resolution structure of dynein-dynactin and the adaptor BICDR1 bound to microtubules. This reveals the asymmetric interactions between neighbouring dynein motor domains and how they relate to motile behaviour. We found that two adaptors occupy the complex. Both adaptors make similar interactions with the dyneins but diverge in their contacts with each other and dynactin. Our structure has implications for the stability and stoichiometry of motor recruitment by cargos.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Studies, Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.