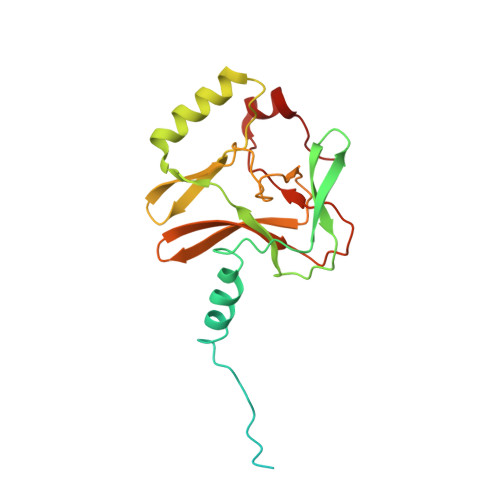
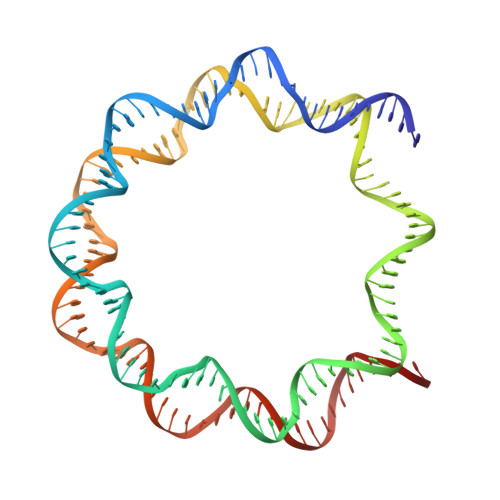
Structural basis of nucleosomal H4K20 methylation by methyltransferase SET8.
Shi, L., Huang, L., Long, H., Song, A., Zhou, Z.(2022) FASEB J 36: e22338-e22338
- PubMed: 35532550
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202101821R
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XPX - PubMed Abstract:
Histone H4 lysine 20 monomethylation (H4K20me1) plays a crucial role in multiple processes including DNA damage repair, DNA replication, and cell cycle control. Histone methyltransferase SET8 (previously named PR-Set7/KMT5A) mediates the chromatin deposition of H4K20me1, but how SET8 recognizes and modifies H4 in the context of the nucleosome is not fully understood. Here, we developed a simple chemical modification approach for H4K20 substitution by using the lysine analog S-ethyl-L-cysteine (Ecx). Substitution of H4K20 with H4Ecx20 improves the stability of the SET8-nucleosome complex, allowing us to determine the cryo-EM structure at 3.2 Å resolution. Structural analyses show that SET8 directly interacts with the H4 tail and the H2A-H2B acidic patch to ensure nucleosome binding. SET8 residues R339, K341, K351 make contact with nucleosomal DNA at the super helical location 2 (SHL2). Substitution of SET8 DNA-binding residues with alanines decreases the SET8-nucleosome interaction and impairs the methyltransferase activity. Disrupting the binding between SET8 R192 and H2A-H2B acidic patch decreases the cellular level of H4K20me1. Together, these results reveal a near-atomic resolution structure of SET8-bound nucleosome and provide insights into the SET8-mediated H4K20 recognition and modification. The lysine-to-Ecx substitution approach can be applied to the study of other methyltransferases.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.