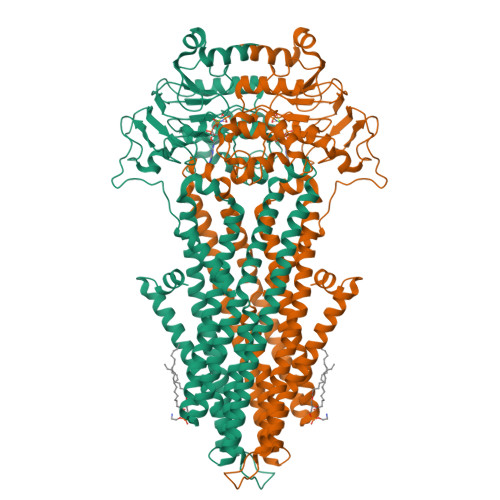
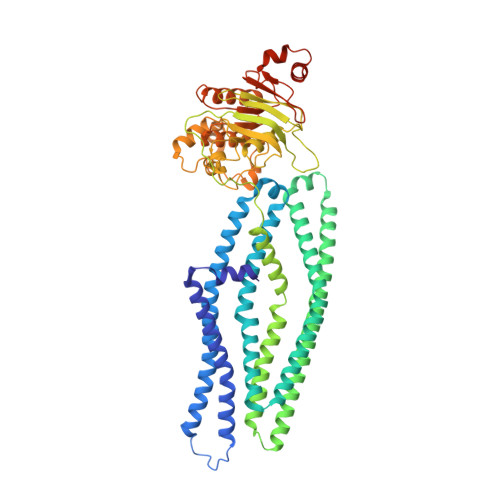
Conformational changes in the yeast mitochondrial ABC transporter Atm1 during the transport cycle.
Ellinghaus, T.L., Marcellino, T., Srinivasan, V., Lill, R., Kuhlbrandt, W.(2021) Sci Adv 7: eabk2392-eabk2392
- PubMed: 34936443
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abk2392
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PSL, 7PSM, 7PSN - PubMed Abstract:
The mitochondrial inner membrane ABC transporter Atm1 exports an unknown substrate to the cytosol for iron-sulfur protein biogenesis, cellular iron regulation, and tRNA thio-modification. Mutations in the human relative ABCB7 cause the iron storage disease XLSA/A. We determined 3D structures of two complementary states of Atm1 in lipid nanodiscs by electron cryo-microscopy at 2.9- to 3.4-Å resolution. The inward-open structure resembled the known crystal structure of nucleotide-free apo-Atm1 closely. The occluded conformation with bound AMP-PNP-Mg 2+ showed a tight association of the two nucleotide-binding domains, a rearrangement of the C-terminal helices, and closure of the putative substrate-binding cavity in the homodimeric transporter. We identified a hydrophobic patch on the C-terminal helices of yeast Atm1, which is unique among type IV ABC transporters of known structure. Truncation mutants of yeast Atm1 suggest that the C-terminal helices stabilize the dimer, yet are not necessary for closure of the nucleotide-binding domains.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck Institute of Biophysics, Max-von-Laue-Str. 3, 60438 Frankfurt, Germany.