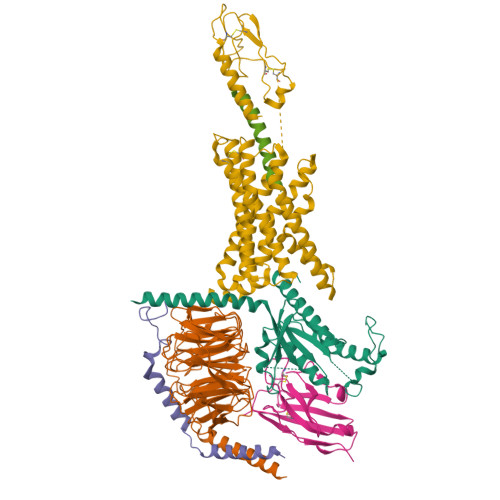
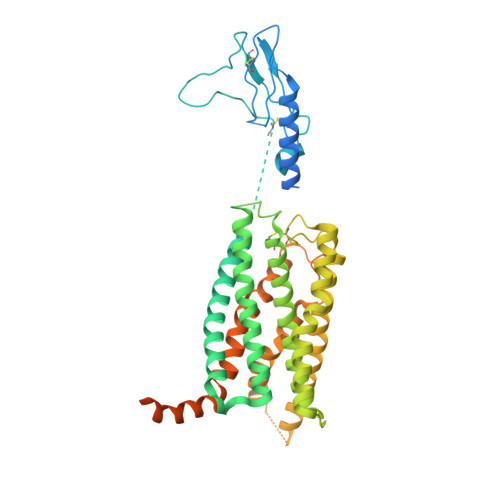
Dynamics of GLP-1R peptide agonist engagement are correlated with kinetics of G protein activation.
Deganutti, G., Liang, Y.L., Zhang, X., Khoshouei, M., Clydesdale, L., Belousoff, M.J., Venugopal, H., Truong, T.T., Glukhova, A., Keller, A.N., Gregory, K.J., Leach, K., Christopoulos, A., Danev, R., Reynolds, C.A., Zhao, P., Sexton, P.M., Wootten, D.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 92-92
- PubMed: 35013280
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27760-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LLL, 7LLY - PubMed Abstract:
The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) has broad physiological roles and is a validated target for treatment of metabolic disorders. Despite recent advances in GLP-1R structure elucidation, detailed mechanistic understanding of how different peptides generate profound differences in G protein-mediated signalling is still lacking. Here we combine cryo-electron microscopy, molecular dynamics simulations, receptor mutagenesis and pharmacological assays, to interrogate the mechanism and consequences of GLP-1R binding to four peptide agonists; glucagon-like peptide-1, oxyntomodulin, exendin-4 and exendin-P5. These data reveal that distinctions in peptide N-terminal interactions and dynamics with the GLP-1R transmembrane domain are reciprocally associated with differences in the allosteric coupling to G proteins. In particular, transient interactions with residues at the base of the binding cavity correlate with enhanced kinetics for G protein activation, providing a rationale for differences in G protein-mediated signalling efficacy from distinct agonists.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Sport, Exercise and Life Sciences, Coventry University, CV1 5FB, Coventry, UK.