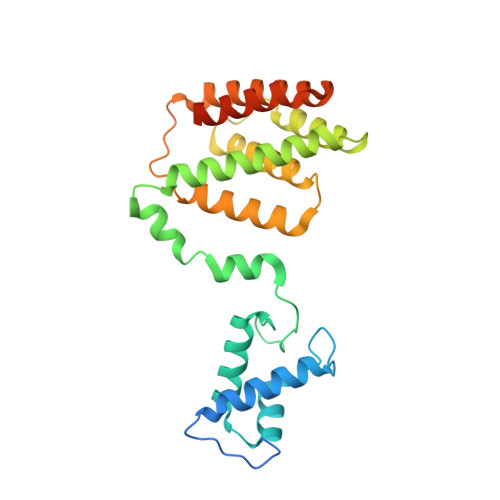
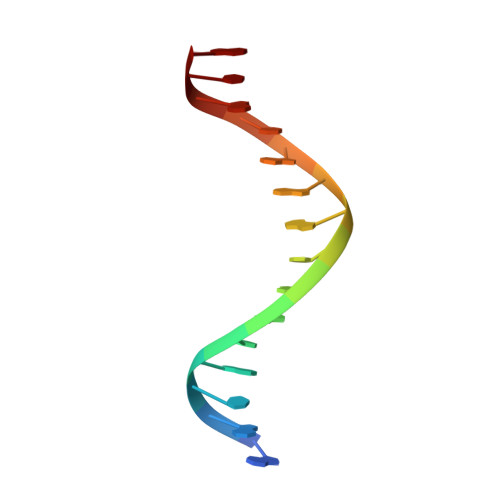
Mechanism of NanR gene repression and allosteric induction of bacterial sialic acid metabolism.
Horne, C.R., Venugopal, H., Panjikar, S., Wood, D.M., Henrickson, A., Brookes, E., North, R.A., Murphy, J.M., Friemann, R., Griffin, M.D.W., Ramm, G., Demeler, B., Dobson, R.C.J.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 1988-1988
- PubMed: 33790291
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22253-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WFQ, 6WG7 - PubMed Abstract:
Bacteria respond to environmental changes by inducing transcription of some genes and repressing others. Sialic acids, which coat human cell surfaces, are a nutrient source for pathogenic and commensal bacteria. The Escherichia coli GntR-type transcriptional repressor, NanR, regulates sialic acid metabolism, but the mechanism is unclear. Here, we demonstrate that three NanR dimers bind a (GGTATA) 3 -repeat operator cooperatively and with high affinity. Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structures reveal the DNA-binding domain is reorganized to engage DNA, while three dimers assemble in close proximity across the (GGTATA) 3 -repeat operator. Such an interaction allows cooperative protein-protein interactions between NanR dimers via their N-terminal extensions. The effector, N-acetylneuraminate, binds NanR and attenuates the NanR-DNA interaction. The crystal structure of NanR in complex with N-acetylneuraminate reveals a domain rearrangement upon N-acetylneuraminate binding to lock NanR in a conformation that weakens DNA binding. Our data provide a molecular basis for the regulation of bacterial sialic acid metabolism.
- Biomolecular Interaction Centre and School of Biological Sciences, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand.
Organizational Affiliation: