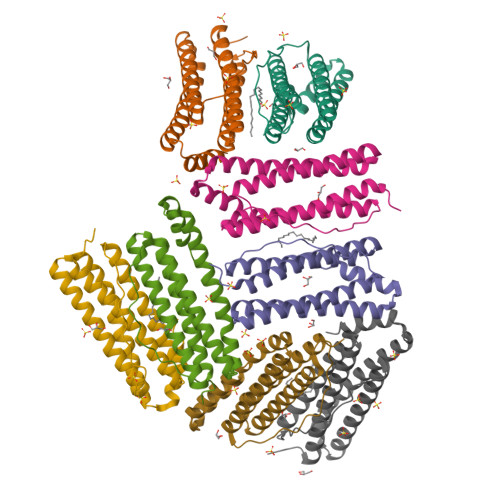
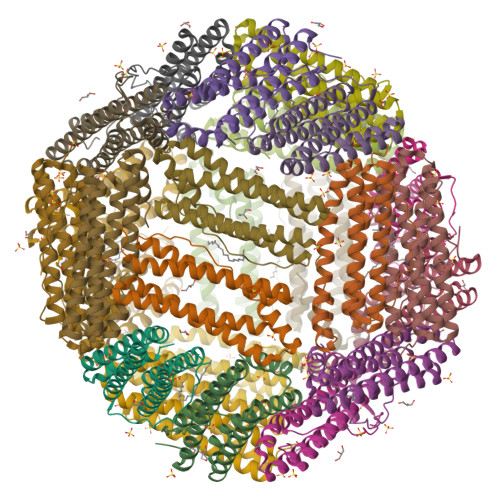
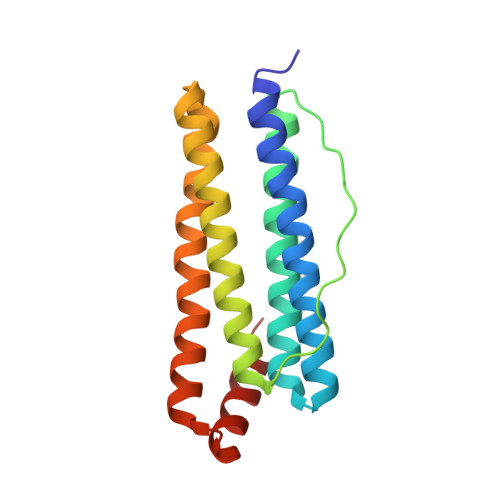
A single residue can modulate nanocage assembly in salt dependent ferritin.
Kumar, M., Markiewicz-Mizera, J., Janna Olmos, J.D., Wilk, P., Grudnik, P., Biela, A.P., Jemiola-Rzeminska, M., Gorecki, A., Chakraborti, S., Heddle, J.G.(2021) Nanoscale 13: 11932-11942
- PubMed: 34195748
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nr01632f
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TXH, 6TXI, 6TXJ, 6TXK, 6TXL, 6TXM, 6TXN - PubMed Abstract:
Cage forming proteins have numerous potential applications in biomedicine and biotechnology, where the iron storage ferritin is a widely used example. However, controlling ferritin cage assembly/disassembly remains challenging, typically requiring extreme conditions incompatible with many desirable cargoes, particularly for more fragile biopharmaceuticals. Recently, a ferritin from the hyperthermophile bacterium Thermotoga maritima (TmFtn) has been shown to have reversible assembly under mild conditions, offering greater potential biocompatibility in terms of cargo access and encapsulation. Like Archeoglobus fulgidus ferritin (AfFtn), TmFtn forms 24mer cages mediated by metal ions (Mg2+). We have solved the crystal structure of the wild type TmFtn and several mutants displaying different assembly/disassembly properties. These data combined with other biophysical studies allow us to suggest candidate interfacial amino acids crucial in controlling assembly. This work deepens our understanding of how these ferritin complexes assemble and is a useful step towards production of triggerable ferritins in which these properties can be finely designed and controlled.
Organizational Affiliation:
Malopolska Centre of Biotechnology, Jagiellonian University, Gronostajowa 7A, 30-392 Krakow, Poland. soumyabiochem@gmail.com Jonathan.heddle@uj.edu.pl.