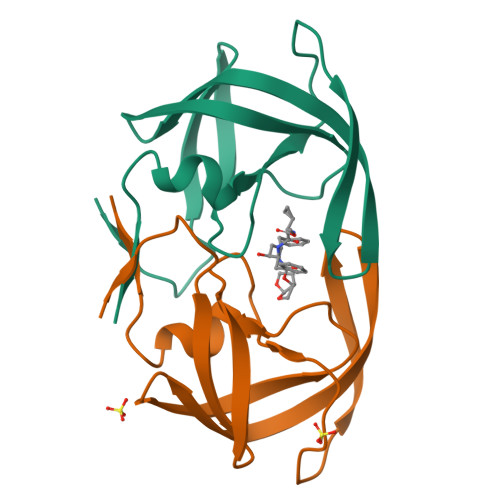
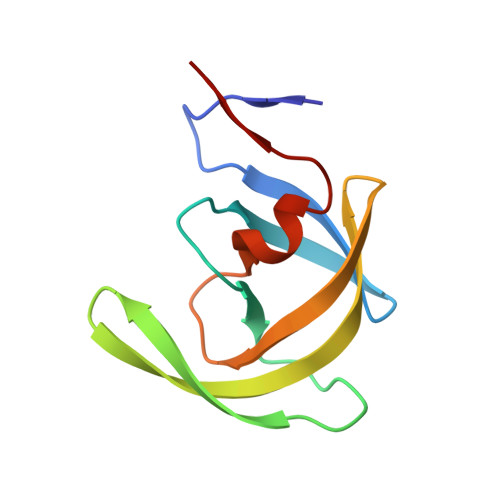
Structural Analysis of Potent Hybrid HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors Containing Bis-tetrahydrofuran in a Pseudosymmetric Dipeptide Isostere.
Rusere, L.N., Lockbaum, G.J., Henes, M., Lee, S.K., Spielvogel, E., Rao, D.N., Kosovrasti, K., Nalivaika, E.A., Swanstrom, R., Kurt Yilmaz, N., Schiffer, C.A., Ali, A.(2020) J Med Chem 63: 8296-8313
- PubMed: 32672965
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00529
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PJB, 6PJC, 6PJD, 6PJE, 6PJF, 6PJG, 6PJH, 6PJI, 6PJK, 6PJL, 6PJM, 6PJN, 6PJO - PubMed Abstract:
The design, synthesis, and X-ray structural analysis of hybrid HIV-1 protease inhibitors (PIs) containing bis-tetrahydrofuran (bis-THF) in a pseudo-C 2 -symmetric dipeptide isostere are described. A series of PIs were synthesized by incorporating bis-THF of darunavir on either side of the Phe-Phe isostere of lopinavir in combination with hydrophobic amino acids on the opposite P2/P2' position. Structure-activity relationship studies indicated that the bis-THF moiety can be attached at either the P2 or P2' position without significantly affecting potency. However, the group on the opposite P2/P2' position had a dramatic effect on potency depending on the size and shape of the side chain. Cocrystal structures of inhibitors with wild-type HIV-1 protease revealed that the bis-THF moiety retained similar interactions as observed in the darunavir-protease complex regardless of the position on the Phe-Phe isostere. Analyses of cocrystal structures and molecular dynamics simulations provide insights into optimizing HIV-1 PIs containing bis-THF in non-sulfonamide dipeptide isosteres.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts 01605, United States.