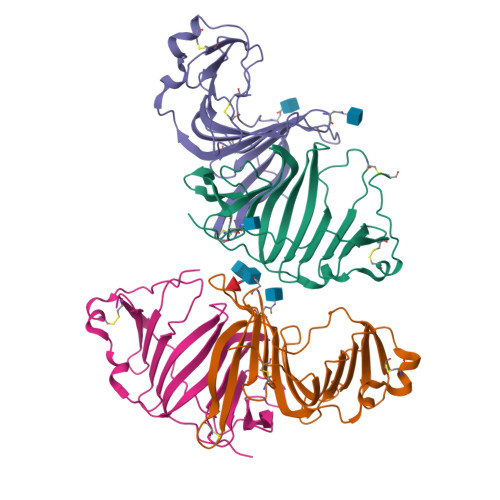
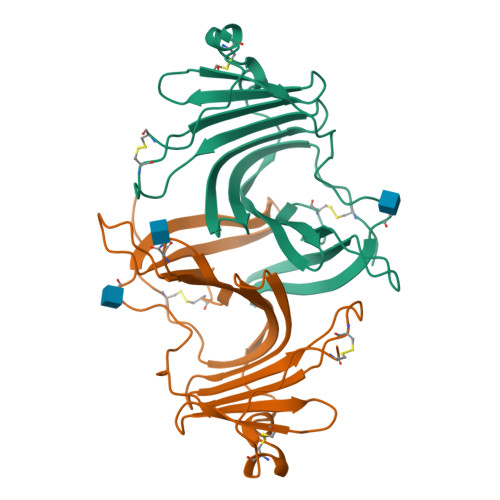
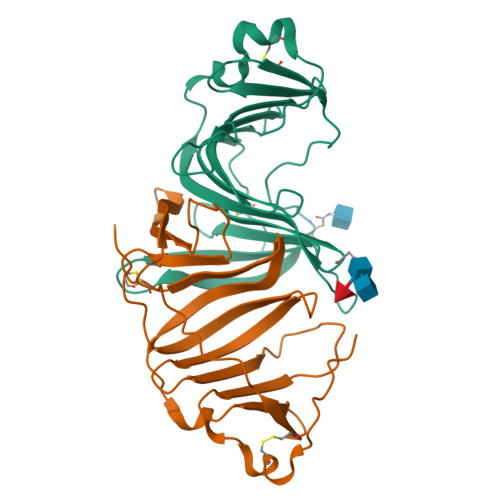
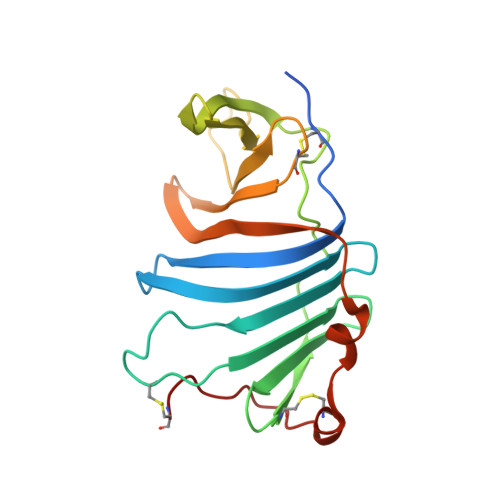
Structures of three ependymin-related proteins suggest their function as a hydrophobic molecule binder.
Park, J.K., Kim, K.Y., Sim, Y.W., Kim, Y.I., Kim, J.K., Lee, C., Han, J., Kim, C.U., Lee, J.E., Park, S.(2019) IUCrJ 6: 729-739
- PubMed: 31316816
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252519007668
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JL9, 6JLA, 6JLD - PubMed Abstract:
Ependymin was first discovered as a predominant protein in brain extracellular fluid in fish and was suggested to be involved in functions mostly related to learning and memory. Orthologous proteins to ependymin called ependymin-related proteins (EPDRs) have been found to exist in various tissues from sea urchins to humans, yet their functional role remains to be revealed. In this study, the structures of EPDR1 from frog, mouse and human were determined and analyzed. All of the EPDR1s fold into a dimer using a monomeric subunit that is mostly made up of two stacking antiparallel β-sheets with a curvature on one side, resulting in the formation of a deep hydrophobic pocket. All six of the cysteine residues in the monomeric subunit participate in the formation of three intramolecular disulfide bonds. Other interesting features of EPDR1 include two asparagine residues with glycosylation and a Ca 2+ -binding site. The EPDR1 fold is very similar to the folds of bacterial VioE and LolA/LolB, which also use a similar hydrophobic pocket for their respective functions as a hydrophobic substrate-binding enzyme and a lipoprotein carrier, respectively. A further fatty-acid binding assay using EPDR1 suggests that it indeed binds to fatty acids, presumably via this pocket. Additional interactome analysis of EPDR1 showed that EPDR1 interacts with insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor and flotillin proteins, which are known to be involved in protein and vesicle translocation.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Systems Biomedical Science, Soongsil University, Seoul 06978, Republic of Korea.