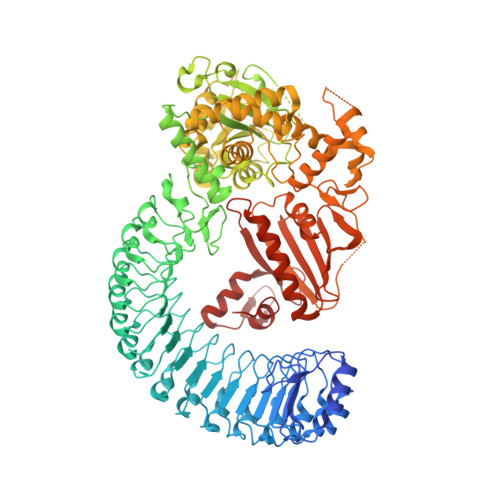
Structure and nucleotide-induced conformational dynamics of theChlorobium tepidumRoco protein.
Deyaert, E., Leemans, M., Singh, R.K., Gallardo, R., Steyaert, J., Kortholt, A., Lauer, J., Versees, W.(2019) Biochem J 476: 51-66
- PubMed: 30538153
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20180803
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HLU - PubMed Abstract:
The LRR (leucine-rich repeat)-Roc (Ras of complex proteins)-COR (C-terminal of Roc) domains are central to the action of nearly all Roco proteins, including the Parkinson's disease-associated protein LRRK2 (leucine-rich repeat kinase 2). We previously demonstrated that the Roco protein from Chlorobium tepidum (CtRoco) undergoes a dimer-monomer cycle during the GTPase reaction, with the protein being mainly dimeric in the nucleotide-free and GDP (guanosine-5'-diphosphate)-bound states and monomeric in the GTP (guanosine-5'-triphosphate)-bound state. Here, we report a crystal structure of CtRoco in the nucleotide-free state showing for the first time the arrangement of the LRR-Roc-COR. This structure reveals a compact dimeric arrangement and shows an unanticipated intimate interaction between the Roc GTPase domains in the dimer interface, involving residues from the P-loop, the switch II loop, the G4 region and a loop which we named the 'Roc dimerization loop'. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange coupled to mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) is subsequently used to highlight structural alterations induced by individual steps along the GTPase cycle. The structure and HDX-MS data propose a pathway linking nucleotide binding to monomerization and relaying the conformational changes via the Roc switch II to the LRR and COR domains. Together, this work provides important new insights in the regulation of the Roco proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
VIB-VUB Center for Structural Biology, Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussels, Belgium.