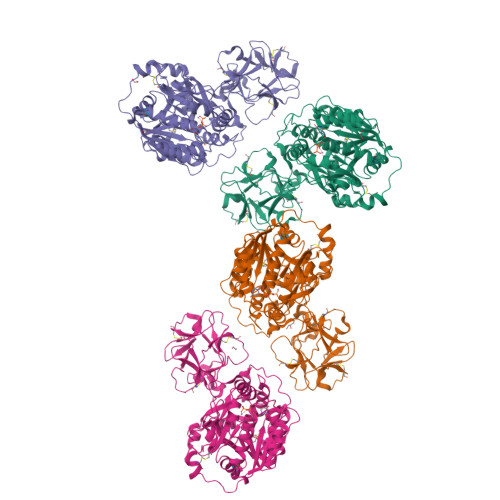
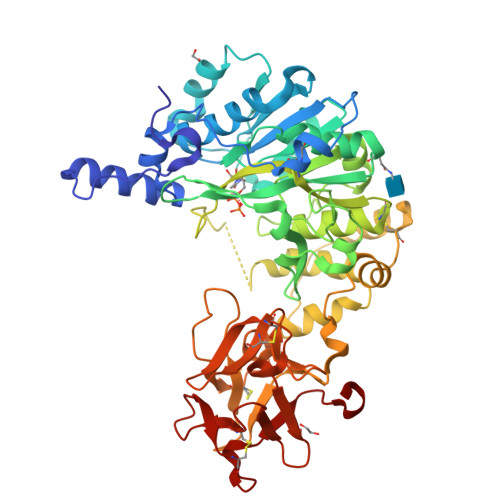
A molecular switch orchestrates enzyme specificity and secretory granule morphology.
Ji, S., Samara, N.L., Revoredo, L., Zhang, L., Tran, D.T., Muirhead, K., Tabak, L.A., Ten Hagen, K.G.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 3508-3508
- PubMed: 30158631
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05978-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6E4Q, 6E4R - PubMed Abstract:
Regulated secretion is an essential process where molecules destined for export are directed to membranous secretory granules, where they undergo packaging and maturation. Here, we identify a gene (pgant9) that influences the structure and shape of secretory granules within the Drosophila salivary gland. Loss of pgant9, which encodes an O-glycosyltransferase, results in secretory granules with an irregular, shard-like morphology, and altered glycosylation of cargo. Interestingly, pgant9 undergoes a splicing event that acts as a molecular switch to alter the charge of a loop controlling access to the active site of the enzyme. The splice variant with the negatively charged loop glycosylates the positively charged secretory cargo and rescues secretory granule morphology. Our study highlights a mechanism for dictating substrate specificity within the O-glycosyltransferase enzyme family. Moreover, our in vitro and in vivo studies suggest that the glycosylation status of secretory cargo influences the morphology of maturing secretory granules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Developmental Glycobiology Section, NIDCR, National Institutes of Health, 30 Convent Drive, Bethesda, MD, 20892-4370, USA.