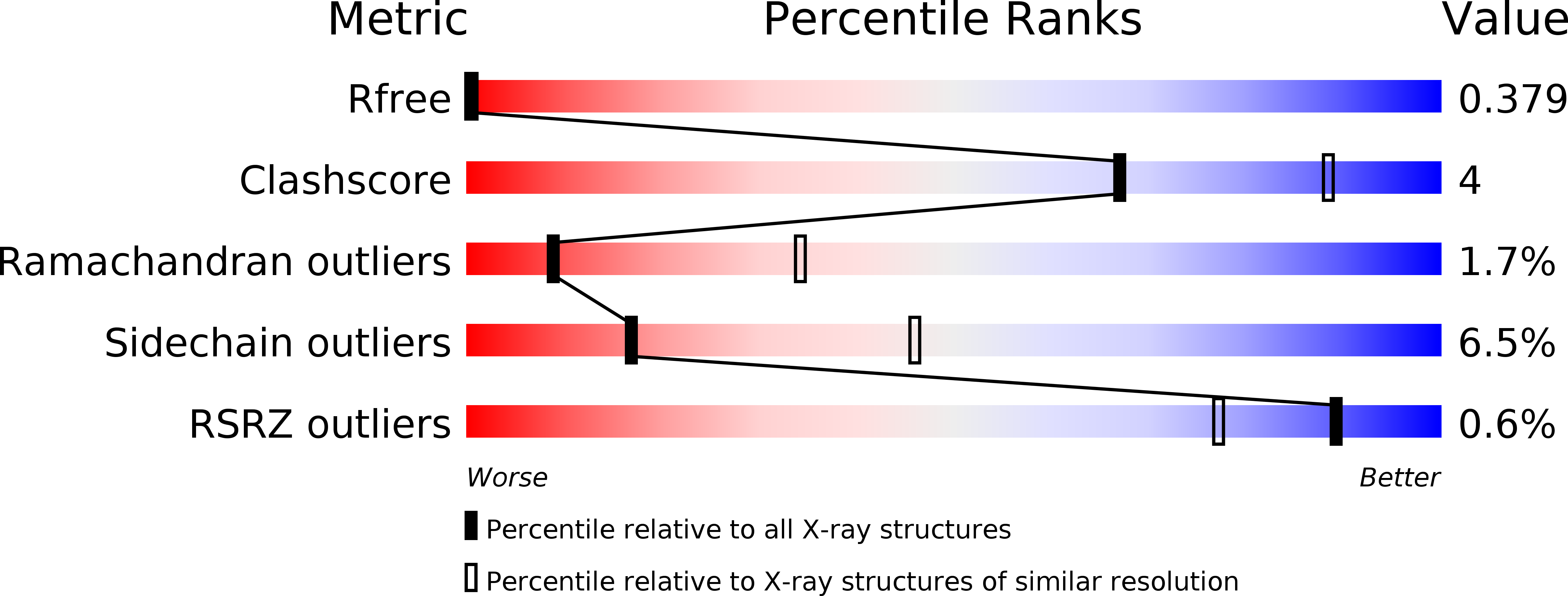
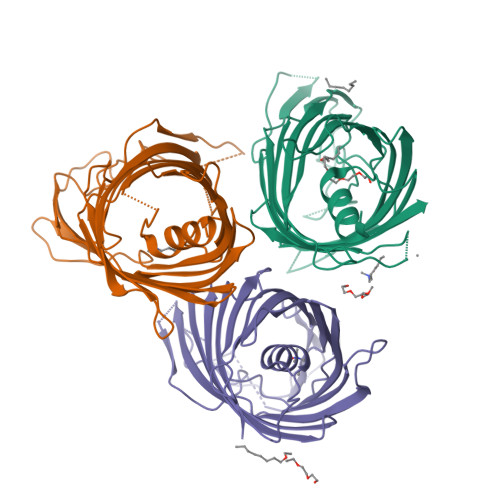
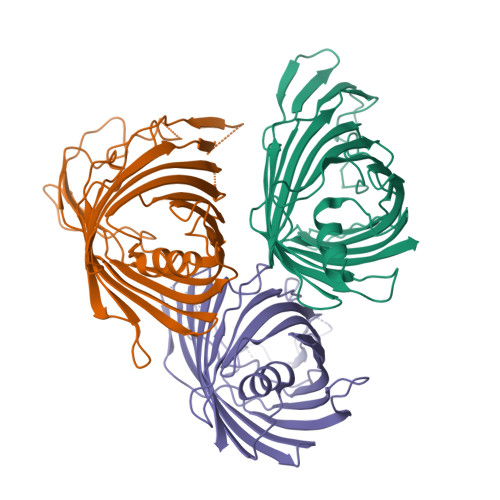
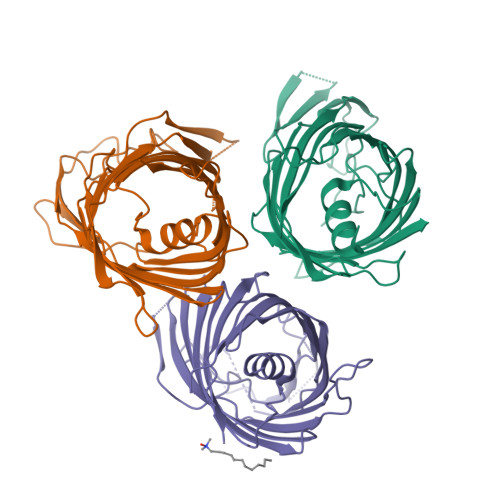
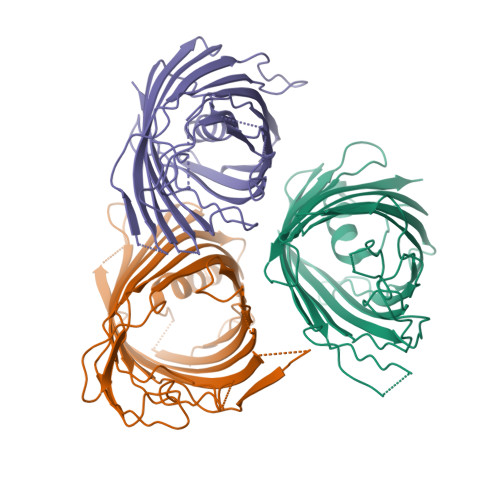
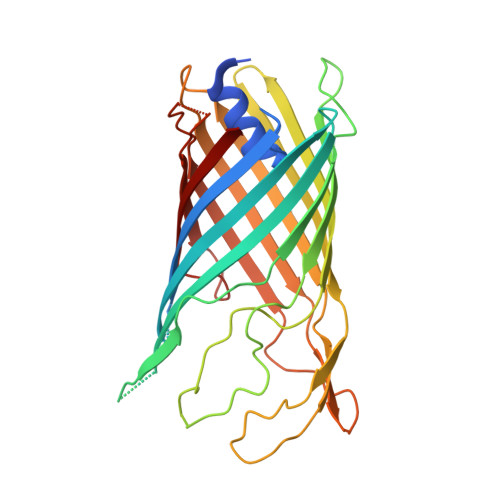
A new class of hybrid secretion system is employed in Pseudomonas amyloid biogenesis.
Rouse, S.L., Hawthorne, W.J., Berry, J.L., Chorev, D.S., Ionescu, S.A., Lambert, S., Stylianou, F., Ewert, W., Mackie, U., Morgan, R.M.L., Otzen, D., Herbst, F.A., Nielsen, P.H., Dueholm, M., Bayley, H., Robinson, C.V., Hare, S., Matthews, S.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 263-263
- PubMed: 28811582
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00361-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5O65, 5O67, 5O68 - PubMed Abstract:
Gram-negative bacteria possess specialised biogenesis machineries that facilitate the export of amyloid subunits for construction of a biofilm matrix. The secretion of bacterial functional amyloid requires a bespoke outer-membrane protein channel through which unfolded amyloid substrates are translocated. Here, we combine X-ray crystallography, native mass spectrometry, single-channel electrical recording, molecular simulations and circular dichroism measurements to provide high-resolution structural insight into the functional amyloid transporter from Pseudomonas, FapF. FapF forms a trimer of gated β-barrel channels in which opening is regulated by a helical plug connected to an extended coil-coiled platform spanning the bacterial periplasm. Although FapF represents a unique type of secretion system, it shares mechanistic features with a diverse range of peptide translocation systems. Our findings highlight alternative strategies for handling and export of amyloid protein sequences.Gram-negative bacteria assemble biofilms from amyloid fibres, which translocate across the outer membrane as unfolded amyloid precursors through a secretion system. Here, the authors characterise the structural details of the amyloid transporter FapF in Pseudomonas.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life Sciences, Imperial College London, South Kensington Campus, London, SW72AZ, UK.