Engineering of anp efficient mutant of Neisseria polysaccharea amylosucrase for the synthesis of controlled size maltooligosaccharides.
Verges, A., Barbe, S., Cambon, E., Moulis, C., Tranier, S., Remaud-Simeon, M., Andre, I.(2017) Carbohydr Polym 173: 403-411
- PubMed: 28732882
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
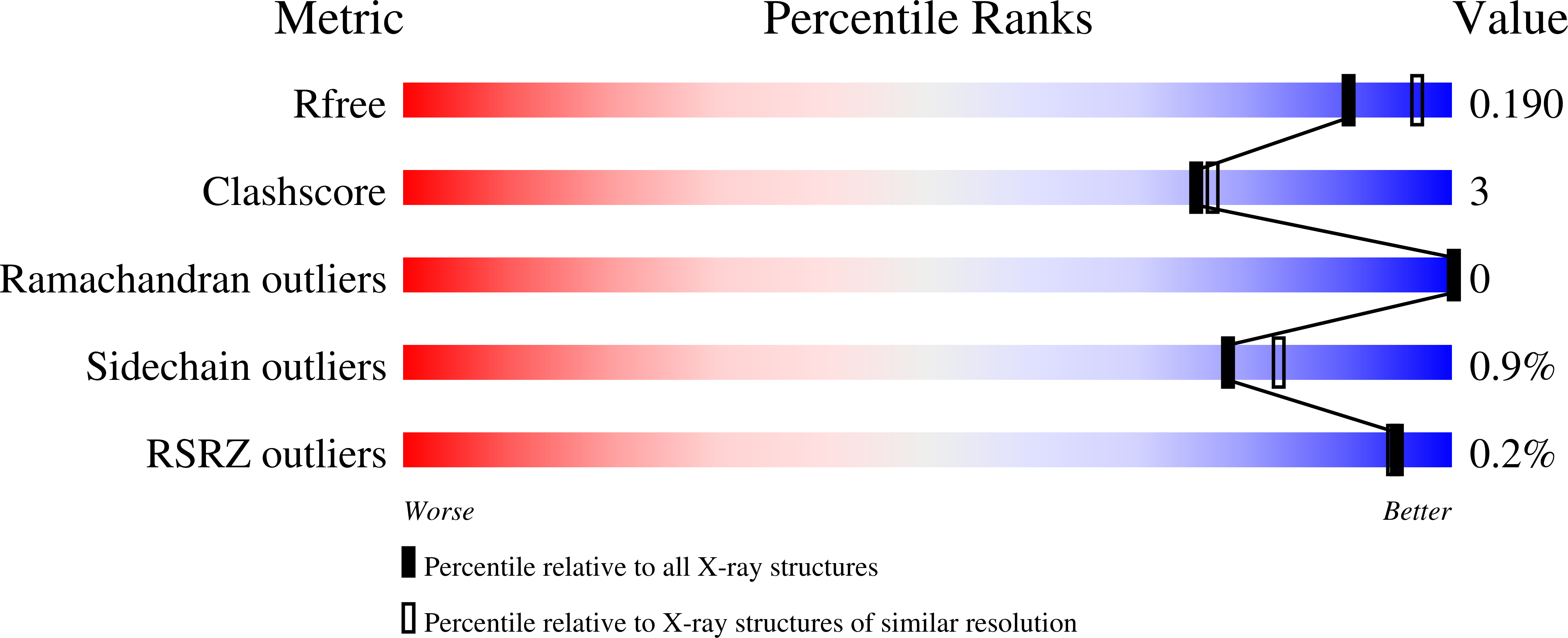
5N7J - PubMed Abstract:
Amylosucrase from Neisseria polysaccharea naturally catalyzes the synthesis of α-1,4 glucans from sucrose. The product profile is quite polydisperse, ranging from soluble chains called maltooligosaccharides to high-molecular weight insoluble amylose. This enzyme was recently subjected to engineering of its active site to enable recognition of non-natural acceptor substrates. Libraries of variants were constructed and screened on sucrose, allowing the identification of a mutant that showed a 6-fold enhanced activity toward sucrose compared to the wild-type enzyme. Furthermore, its product profile was unprecedented, as only soluble maltooligosaccharides of controlled size chains (2
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire d'Ingénierie des Systèmes Biologiques et des Procédés, Université de Toulouse, CNRS, INRA, INSA, 31400 Toulouse, France.