Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms of two nanobodies that inhibit thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor activation and activated thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor activity.
Zhou, X., Weeks, S.D., Ameloot, P., Callewaert, N., Strelkov, S.V., Declerck, P.J.(2016) J Thromb Haemost 14: 1629-1638
- PubMed: 27279497
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.13381
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HVF, 5HVG, 5HVH - PubMed Abstract:
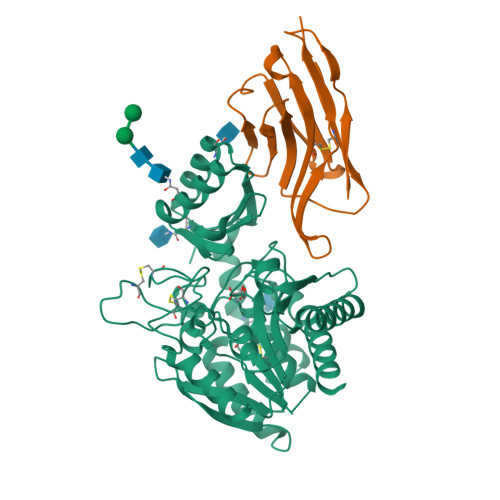
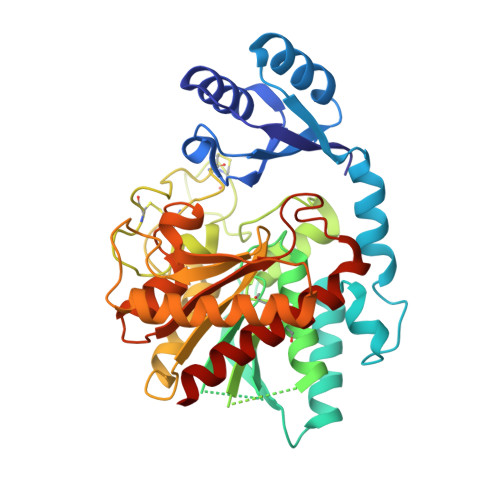
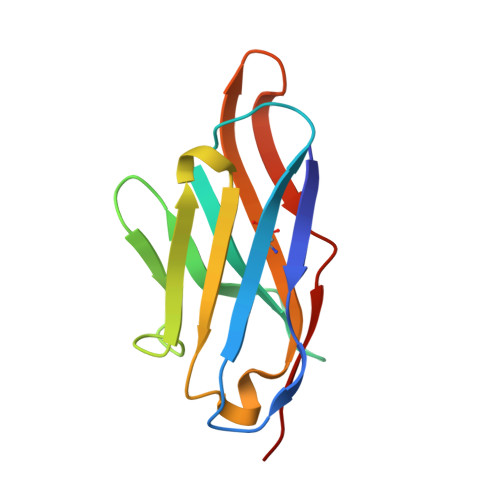
Essentials Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) is a risk factor for cardiovascular disorders. TAFI inhibitory nanobodies represent a promising step in developing profibrinolytic therapeutics. We have solved three crystal structures of TAFI in complex with inhibitory nanobodies. Nanobodies inhibit TAFI through distinct mechanisms and represent novel profibrinolytic leads. Background Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) is converted to activated TAFI (TAFIa) by thrombin, plasmin, or the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex (T/TM). TAFIa is antifibrinolytic, and high levels of TAFIa are associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disorders. TAFI-inhibitory nanobodies represent a promising approach for developing profibrinolytic therapeutics. Objective To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of inhibition of TAFI activation and TAFIa activity by nanobodies with the use of X-ray crystallography and biochemical characterization. Methods and results We selected two nanobodies for cocrystallization with TAFI. VHH-a204 interferes with all TAFI activation modes, whereas VHH-i83 interferes with T/TM-mediated activation and also inhibits TAFIa activity. The 3.05-Å-resolution crystal structure of TAFI-VHH-a204 reveals that the VHH-a204 epitope is localized to the catalytic moiety (CM) in close proximity to the TAFI activation site at Arg92, indicating that VHH-a204 inhibits TAFI activation by steric hindrance. The 2.85-Å-resolution crystal structure of TAFI-VHH-i83 reveals that the VHH-i83 epitope is located close to the presumptive thrombomodulin-binding site in the activation peptide (AP). The structure and supporting biochemical assays suggest that VHH-i83 inhibits TAFIa by bridging the AP to the CM following TAFI activation. In addition, the 3.00-Å-resolution crystal structure of the triple TAFI-VHH-a204-VHH-i83 complex demonstrates that the two nanobodies can simultaneously bind to TAFI. Conclusions This study provides detailed insights into the molecular mechanisms of TAFI inhibition, and reveals a novel mode of TAFIa inhibition. VHH-a204 and VHH-i83 merit further evaluation as potential profibrinolytic therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical and Pharmacologic Sciences, Laboratory for Therapeutic and Diagnostic Antibodies, KU Leuven, Belgium.