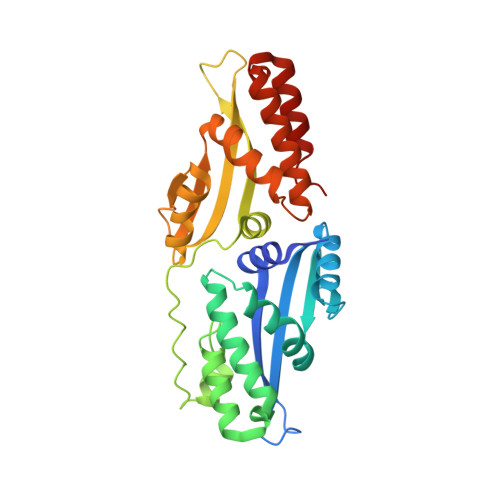
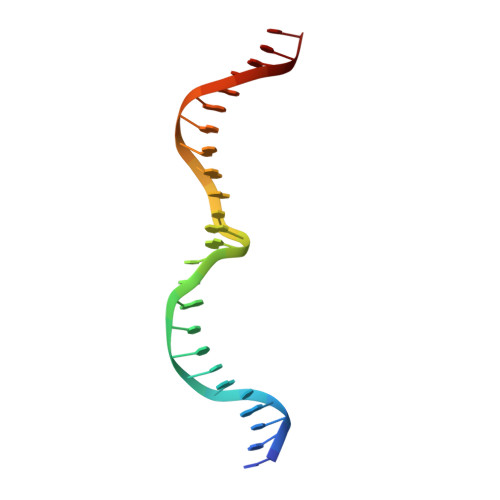
The Structural Basis of Asymmetry in DNA Binding and Cleavage as Exhibited by the I-SmaMI LAGLIDADG Meganuclease.
Shen, B.W., Lambert, A., Walker, B.C., Stoddard, B.L., Kaiser, B.K.(2016) J Mol Biol 428: 206-220
- PubMed: 26705195
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2015.12.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5E5O, 5E5P, 5E5S, 5E63, 5E67 - PubMed Abstract:
LAGLIDADG homing endonucleases ("meganucleases") are highly specific DNA cleaving enzymes that are used for genome engineering. Like other enzymes that act on DNA targets, meganucleases often display binding affinities and cleavage activities that are dominated by one protein domain. To decipher the underlying mechanism of asymmetric DNA recognition and catalysis, we identified and characterized a new monomeric meganuclease (I-SmaMI), which belongs to a superfamily of homologous enzymes that recognize divergent DNA sequences. We solved a series of crystal structures of the enzyme-DNA complex representing a progression of sequential reaction states, and we compared the structural rearrangements and surface potential distributions within each protein domain against their relative contribution to binding affinity. We then determined the effects of equivalent point mutations in each of the two enzyme active sites to determine whether asymmetry in DNA recognition is translated into corresponding asymmetry in DNA cleavage activity. These experiments demonstrate the structural basis for "dominance" by one protein domain over the other and provide insights into this enzyme's conformational switch from a nonspecific search mode to a more specific recognition mode.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Basic Sciences, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, 1100 Fairview Avenue North, Seattle, WA 98109, USA. Electronic address: bshen@fredhutch.org.