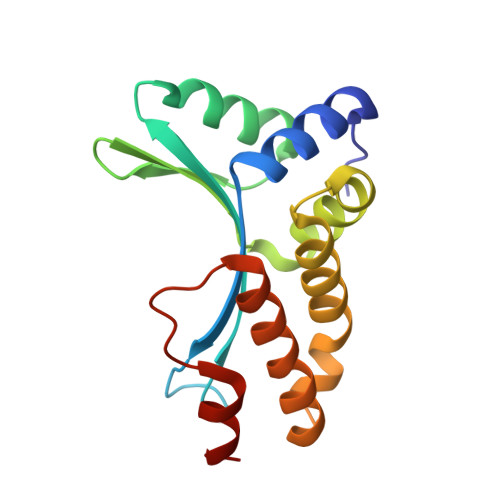
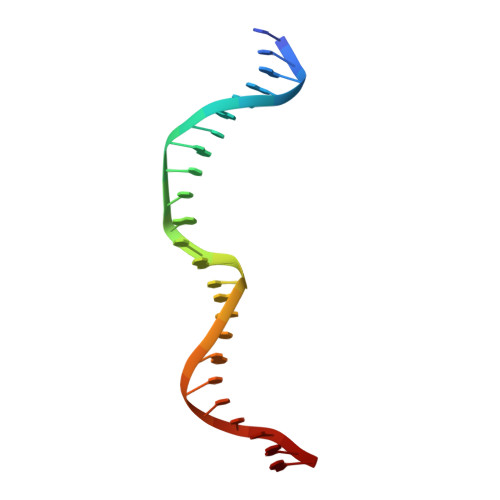
Non-Specific Protein-DNA Interactions Control I-Crei Target Binding and Cleavage.
Molina, R., Redondo, P., Stella, S., Marenchino, M., D'Abramo, M., Gervasio, F.L., Charles Epinat, J., Valton, J., Grizot, S., Duchateau, P., Prieto, J., Montoya, G.(2012) Nucleic Acids Res 40: 6936-6945
- PubMed: 22495931
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks320
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AAB, 4AAD, 4AAE, 4AAF, 4AAG - PubMed Abstract:
Homing endonucleases represent protein scaffolds that provide powerful tools for genome manipulation, as these enzymes possess a very low frequency of DNA cleavage in eukaryotic genomes due to their high specificity. The basis of protein-DNA recognition must be understood to generate tailored enzymes that target the DNA at sites of interest. Protein-DNA interaction engineering of homing endonucleases has demonstrated the potential of these approaches to create new specific instruments to target genes for inactivation or repair. Protein-DNA interface studies have been focused mostly on specific contacts between amino acid side chains and bases to redesign the binding interface. However, it has been shown that 4 bp in the central DNA sequence of the 22-bp substrate of a homing endonuclease (I-CreI), which do not show specific protein-DNA interactions, is not devoid of content information. Here, we analyze the mechanism of target discrimination in this substrate region by the I-CreI protein, determining how it can occur independently of the specific protein-DNA interactions. Our data suggest the important role of indirect readout in this substrate region, opening the possibility for a fully rational search of new target sequences, thus improving the development of redesigned enzymes for therapeutic and biotechnological applications.
- Structural Biology and Biocomputing Programme, Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), Macromolecular Crystallography Group, Madrid, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: