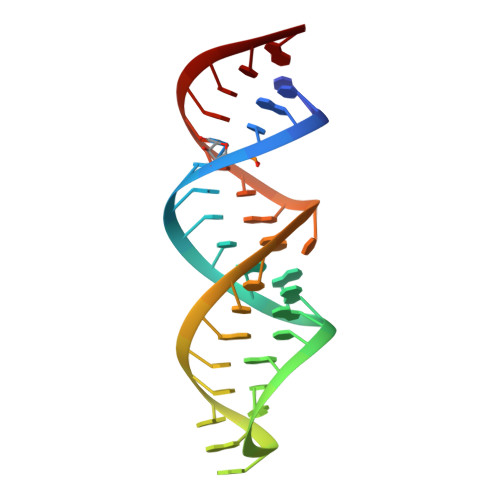
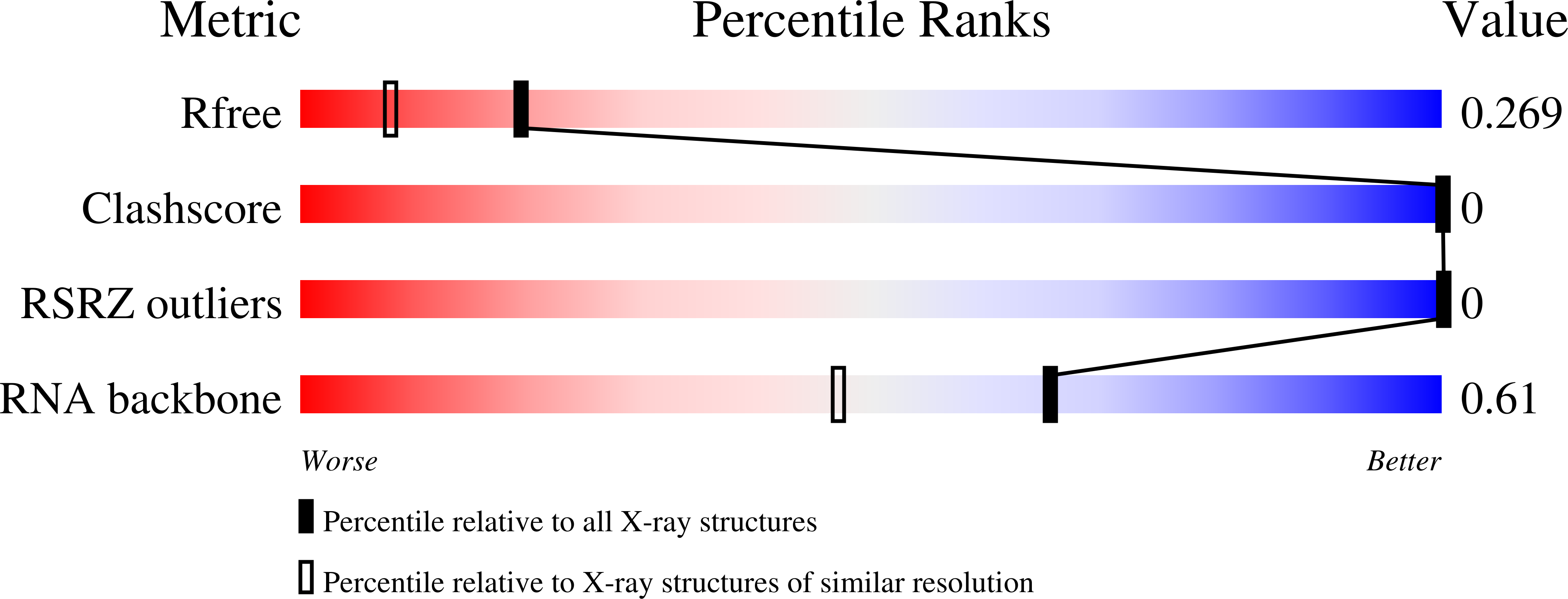Modifications to toxic CUG RNAs induce structural stability, rescue mis-splicing in a myotonic dystrophy cell model and reduce toxicity in a myotonic dystrophy zebrafish model.
deLorimier, E., Coonrod, L.A., Copperman, J., Taber, A., Reister, E.E., Sharma, K., Todd, P.K., Guenza, M.G., Berglund, J.A.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 12768-12778
- PubMed: 25303993
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku941
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PCJ - PubMed Abstract:
CUG repeat expansions in the 3' UTR of dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) cause myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). As RNA, these repeats elicit toxicity by sequestering splicing proteins, such as MBNL1, into protein-RNA aggregates. Structural studies demonstrate that CUG repeats can form A-form helices, suggesting that repeat secondary structure could be important in pathogenicity. To evaluate this hypothesis, we utilized structure-stabilizing RNA modifications pseudouridine (Ψ) and 2'-O-methylation to determine if stabilization of CUG helical conformations affected toxicity. CUG repeats modified with Ψ or 2'-O-methyl groups exhibited enhanced structural stability and reduced affinity for MBNL1. Molecular dynamics and X-ray crystallography suggest a potential water-bridging mechanism for Ψ-mediated CUG repeat stabilization. Ψ modification of CUG repeats rescued mis-splicing in a DM1 cell model and prevented CUG repeat toxicity in zebrafish embryos. This study indicates that the structure of toxic RNAs has a significant role in controlling the onset of neuromuscular diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Institute of Molecular Biology, University of Oregon, Eugene, Oregon, USA.