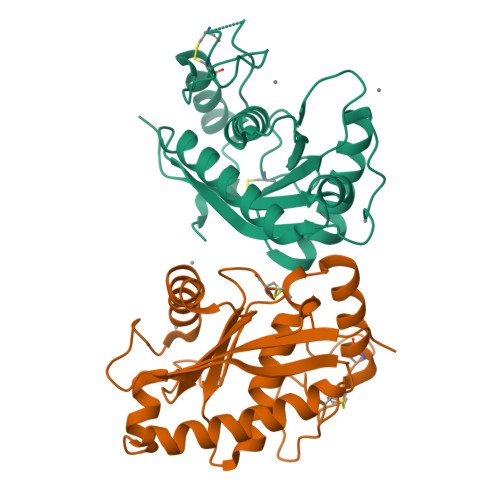
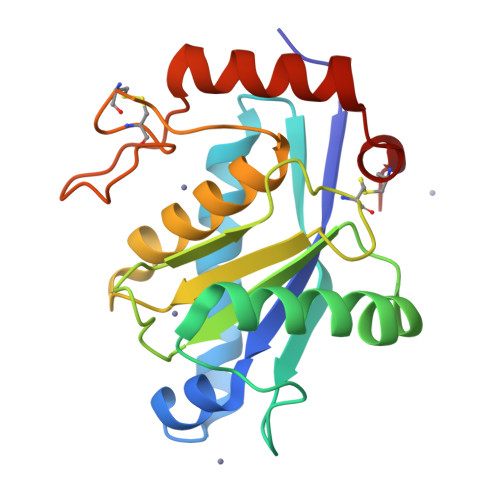
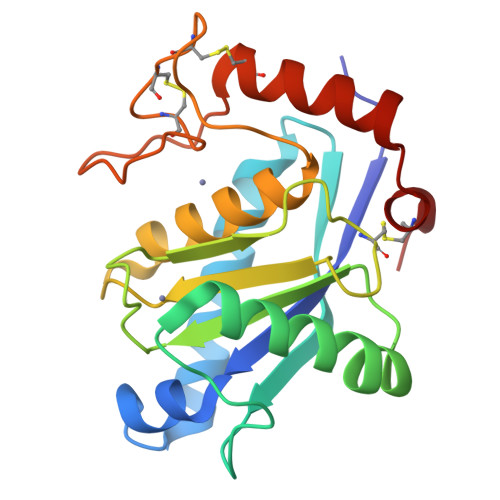
Crystal structure of a Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus venom metalloproteinase providing new insights into the inhibition by endogenous tripeptide inhibitors.
Chou, T.L., Wu, C.H., Huang, K.F., Wang, A.H.(2013) Toxicon 71C: 140-146
- PubMed: 23732127
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.05.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4J4M - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of TM-1, a P-I class snake-venom metalloproteinase (SVMP) from the Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus venom, was determined at 1.8-Å resolution. The structure exhibits the typical feature of SVMPs and is stabilized by three disulfide linkages. The active site shows a deep S1' substrate-binding pocket limited by the non-conserved Pro174 at the bottom. Further comparisons with other SVMPs suggest that the deep S1' site of TM-1 correlates with its high inhibition sensitivity to the endogenous tripeptide inhibitors. Proteolytic specificity analysis revealed that TM-1 prefers substrates having a moderate-size and hydrophobic residue at the P1' position, consistent with our structural observation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemical Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei 10617, Taiwan.