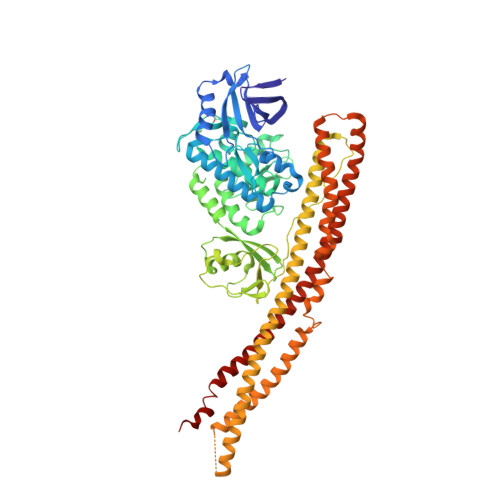
Crystal structure and mechanism of activation of TANK-binding kinase 1.
Larabi, A., Devos, J.M., Ng, S.L., Nanao, M.H., Round, A., Maniatis, T., Panne, D.(2013) Cell Rep 3: 734-746
- PubMed: 23453971
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.01.034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4IW0, 4IWO, 4IWP, 4IWQ - PubMed Abstract:
Tank-binding kinase I (TBK1) plays a key role in the innate immune system by integrating signals from pattern-recognition receptors. Here, we report the X-ray crystal structures of inhibitor-bound inactive and active TBK1 determined to 2.6 Å and 4.0 Å resolution, respectively. The structures reveal a compact dimer made up of trimodular subunits containing an N-terminal kinase domain (KD), a ubiquitin-like domain (ULD), and an α-helical scaffold dimerization domain (SDD). Activation rearranges the KD into an active conformation while maintaining the overall dimer conformation. Low-resolution SAXS studies reveal that the missing C-terminal domain (CTD) extends away from the main body of the kinase dimer. Mutants that interfere with TBK1 dimerization show significantly reduced trans-autophosphorylation but retain the ability to bind adaptor proteins through the CTD. Our results provide detailed insights into the architecture of TBK1 and the molecular mechanism of activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
EMBL Grenoble, 6 Rue Jules Horowitz, Grenoble 38042, France.