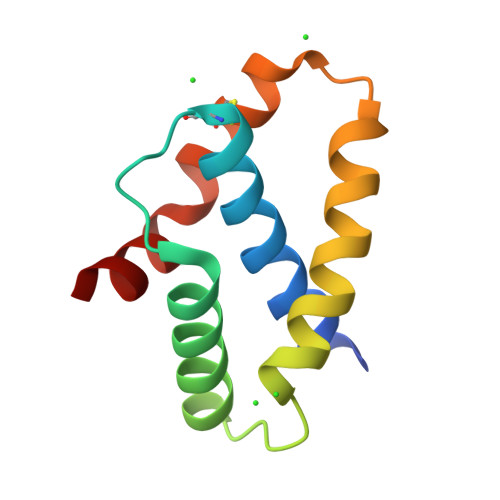
Crystal structure of the pilotin from the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli type II secretion system.
Korotkov, K.V., Hol, W.G.(2013) J Struct Biol 182: 186-191
- PubMed: 23458689
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2013.02.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SOL - PubMed Abstract:
Bacteria contain several sophisticated macromolecular machineries responsible for translocating proteins across the cell envelope. One prominent example is the type II secretion system (T2SS), which contains a large outer membrane channel, called the secretin. These gated channels require specialized proteins, so-called pilotins, to reach and assemble in the outer membrane. Here we report the crystal structure of the pilotin GspS from the T2SS of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC), an important pathogen that can cause severe disease in cases of food poisoning. In this four-helix protein, the straight helix α2, the curved helix α3 and the bent helix α4 surround the central N-terminal helix α1. The helices of GspS create a prominent groove, mainly formed by side chains of helices α1, α2 and α3. In the EHEC GspS structure this groove is occupied by extra electron density which is reminiscent of an α-helix and corresponds well with a binding site observed in a homologous pilotin. The residues forming the groove are well conserved among homologs, pointing to a key role of this groove in this class of T2SS pilotins. At the same time, T2SS pilotins in different species can be entirely different in structure, and the pilotins for secretins in non-T2SS machineries have yet again unrelated folds, despite a common function. It is striking that a common complex function, such as targeting and assembling an outer membrane multimeric channel, can be performed by proteins with entirely different folds.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biomolecular Structure Center, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.