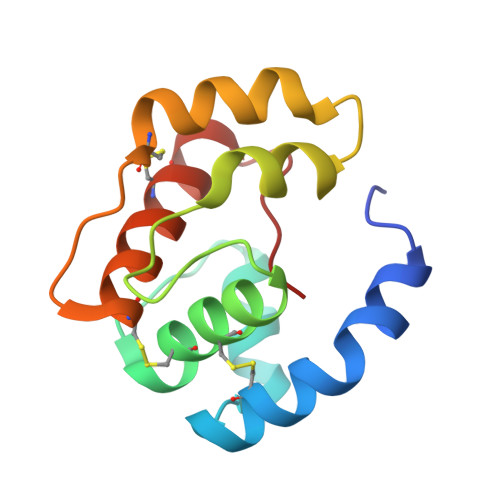
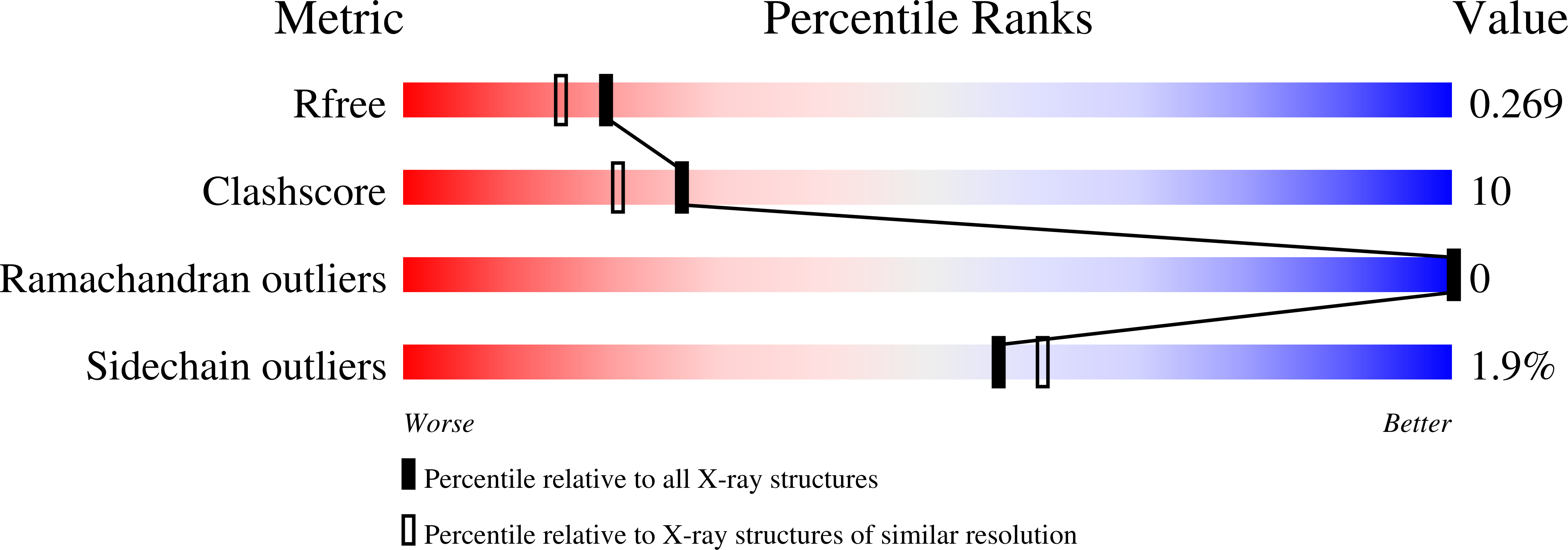Structural basis of the honey bee PBP pheromone and pH-induced conformational change
Pesenti, M.E., Spinelli, S., Bezirard, V., Briand, L., Pernollet, J.C., Tegoni, M., Cambillau, C.(2008) J Mol Biol 380: 158-169
- PubMed: 18508083
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.048
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BFA, 3BFB, 3BFH, 3CAB, 3CDN - PubMed Abstract:
The behavior of insects and their perception of their surroundings are driven, in a large part, by odorants and pheromones. This is especially true for social insects, such as the honey bee, where the queen controls the development and the caste status of the other individuals. Pheromone perception is a complex phenomenon relying on a cascade of recognition events, initiated in antennae by pheromone recognition by a pheromone-binding protein and finishing with signal transduction at the axon membrane level. With to the objective of deciphering this initial step, we have determined the structures of the bee antennal pheromone-binding protein (ASP1) in the apo form and in complex with the main component of the queen mandibular pheromonal mixture, 9-keto-2(E)-decenoic acid (9-ODA) and with nonpheromonal components. In the apo protein, the C terminus obstructs the binding site. In contrast, ASP1 complexes have different open conformations, depending on the ligand shape, leading to different volumes of the binding cavity. The binding site integrity depends on the C terminus (111-119) conformation, which involves the interplay of two factors; i.e. the presence of a ligand and a low pH. Ligand binding to ASP1 is favored by low pH, opposite to what is observed with other pheromone-binding proteins, such as those of Bombyx mori and Anopheles gambiae.
Organizational Affiliation:
Architecture et Fonction des Macromolécules Biologiques, UMR 6098 CNRS and Universités de Marseille, Marseille, France.