Extended Substrate Recognition in Caspase-3 Revealed by High Resolution X-Ray Structure Analysis
Ganesan, R., Mittl, P.R.E., Jelakovic, S., Grutter, M.G.(2006) J Mol Biology 359: 1378
- PubMed: 16787777
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.04.051
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2CJX, 2CJY, 2DKO - PubMed Abstract:
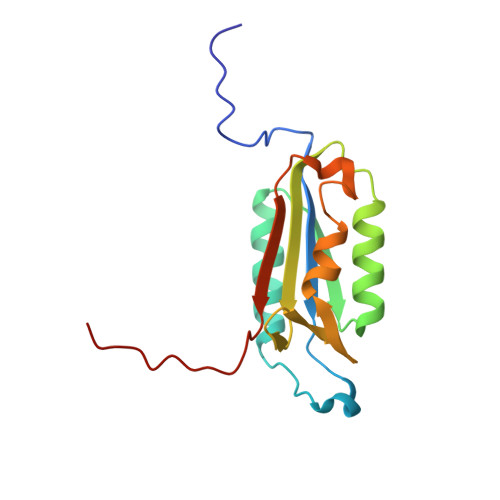
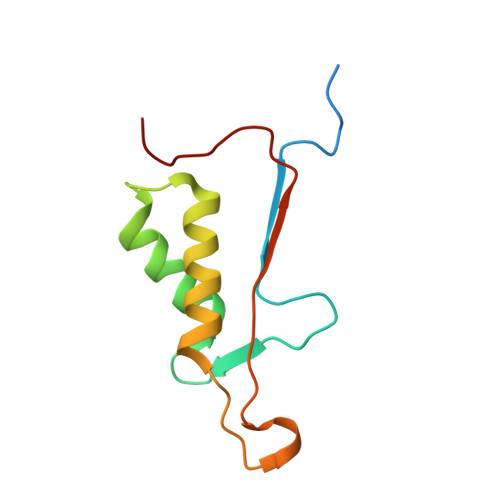
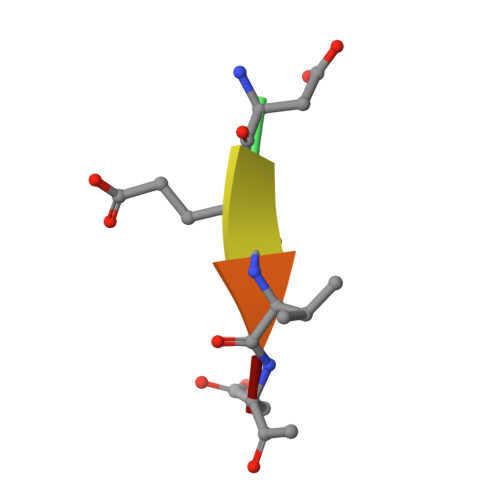
Caspases are cysteine proteases involved in the signalling cascades of programmed cell death in which caspase-3 plays a central role, since it propagates death signals from intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli to downstream targets. The atomic resolution (1.06 Angstroms) crystal structure of the caspase-3 DEVD-cmk complex reveals the structural basis for substrate selectivity in the S4 pocket. A low-barrier hydrogen bond is observed between the side-chains of the P4 inhibitor aspartic acid and Asp179 of the N-terminal tail of the symmetry related p12 subunit. Site-directed mutagenesis of Asp179 confirmed the significance of this residue in substrate recognition. In the 1.06 Angstroms crystal structure, a radiation damage induced rearrangement of the inhibitor methylketone moiety was observed. The carbon atom that in a substrate would represent the scissile peptide bond carbonyl carbon clearly shows a tetrahedral coordination and resembles the postulated tetrahedral intermediate of the acylation reaction.
- Biochemisches Institut, Universität Zürich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: