A novel interaction between atrophin-interacting protein 4 and beta-p21-activated kinase-interactive exchange factor is mediated by an SH3 domain.
Janz, J.M., Sakmar, T.P., Min, K.C.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 28893-28903
- PubMed: 17652093
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M702678200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
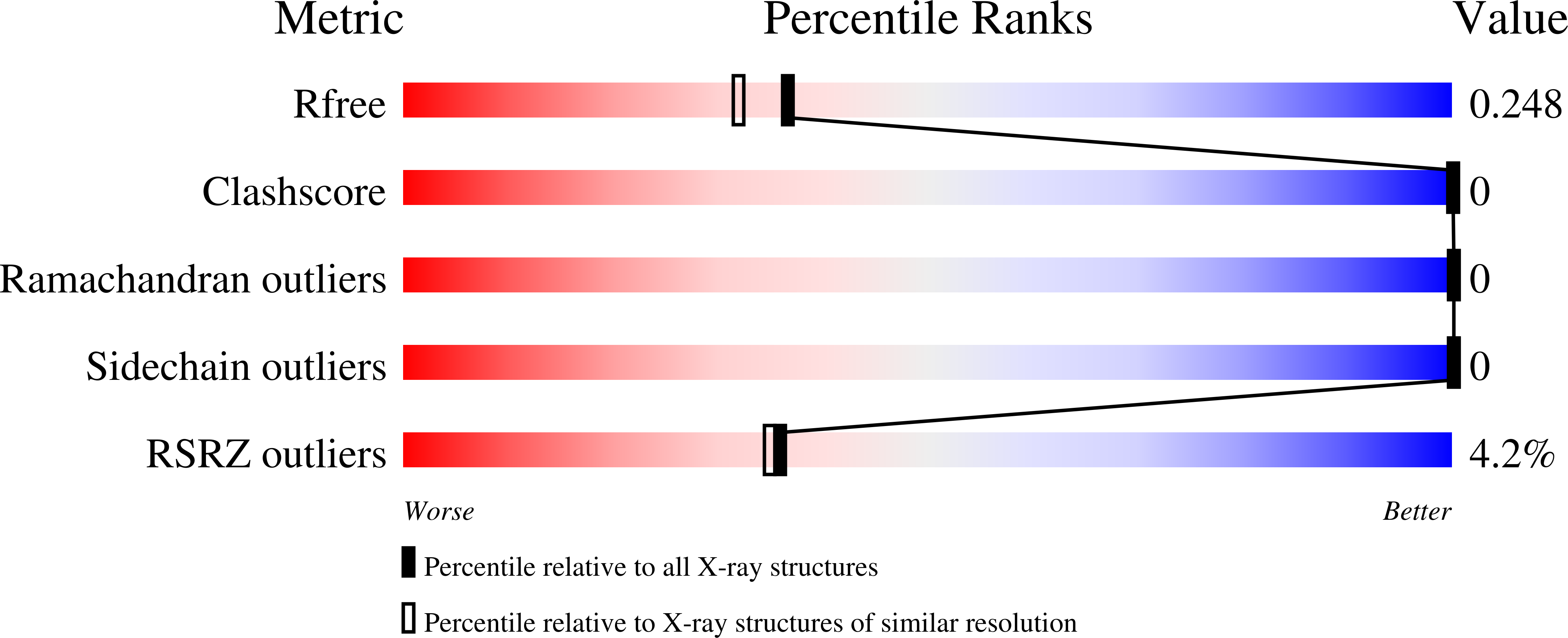
2P4R - PubMed Abstract:
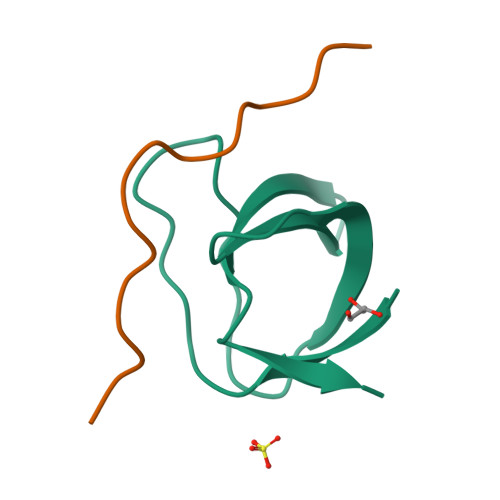
Cross-talk between G protein-coupled receptors and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathways is crucial to the efficient relay and integration of cellular information. Here we identify and define the novel binding interaction of the E3 ubiquitin ligase atrophin-interacting protein 4 (AIP4) with the GTP exchange factor beta-p21-activated kinase-interactive exchange factor (beta PIX). We demonstrate that this interaction is mediated in part by the beta PIX-SH3 domain binding to a proline-rich stretch of AIP4. Analysis of the interaction by isothermal calorimetry is consistent with a heterotrimeric complex with one AIP4-derived peptide binding to two beta PIX-SH3 domains. We determined the crystal structure of the beta PIX-SH3.AIP4 complex to 2.0-A resolution. In contrast to the calorimetry results, the crystal structure shows a monomeric complex in which AIP4 peptide binds the beta PIX-SH3 domain as a canonical Class I ligand with an additional type II polyproline helix that makes extensive contacts with another face of beta PIX. Taken together, the novel interaction between AIP4 and beta PIX represents a new regulatory node for G protein-coupled receptor and receptor tyrosine kinase signal integration. Our structure of the beta PIX-SH3.AIP4 complex provides important insight into the mechanistic basis for beta PIX scaffolding of signaling components, especially those involved in cross-talk.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, The Rockefeller University, New York, New York 10021. Electronic address: jjanz@rockefeller.edu.