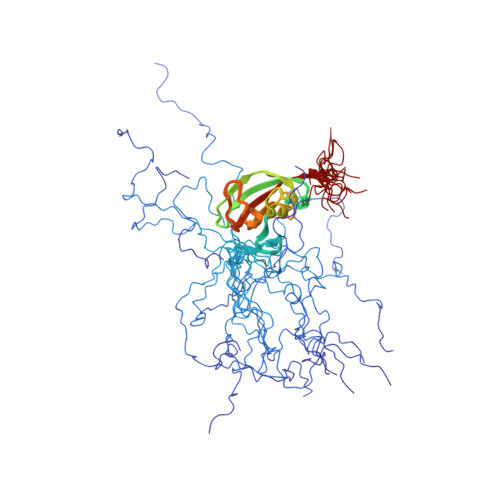
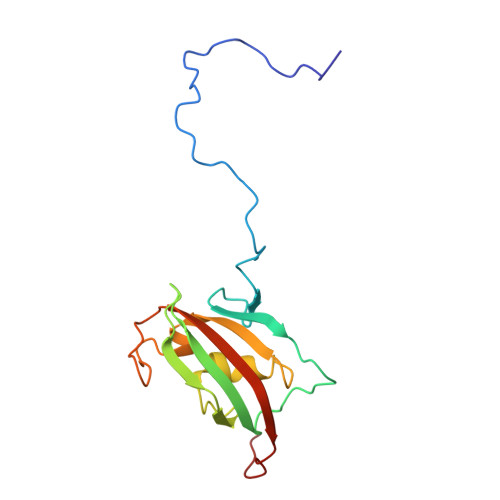
Functional role of the flexible N-terminal extension of FKBP38 in catalysis.
Kang, C., Ye, H., Chia, J., Choi, B.H., Dhe-Paganon, S., Simon, B., Schutz, U., Sattler, M., Yoon, H.S.(2013) Sci Rep 3: 2985-2985
- PubMed: 24145868
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02985
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MF9 - PubMed Abstract:
FKBP38 regulates apoptosis through unique interactions with multiple regulators including Bcl-2. Interestingly, the peptidylprolyl isomerase activity of FKBP38 is only detectable when it binds to calcium-saturated calmodulin (CaM/Ca(2+)). This, in turn, permits the formation of a complex with Bcl-2. FKBP38 thereby provides an important link between isomerase activity and apoptotic pathways. Here, we show that the N-terminal extension (residues 1-32) preceding the catalytic domain of FKBP38 has an autoinhibitory activity. The core isomerase activity of FKBP38 is inhibited by transient interactions involving the flexible N-terminal extension that precedes the catalytic domain. Notably, CaM/Ca(2+) binds to this N-terminal extension and thereby releases the autoinhibitory contacts between the N-terminal extension and the catalytic domain, thus potentiating the isomerase activity of FKBP38. Our data demonstrate how CaM/Ca(2+) modulates the catalytic activity of FKBP38.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] School of Biological Science, Nanyang Technological University, 60 Nanyang Drive, Singapore 637551, Singapore [2] [3].