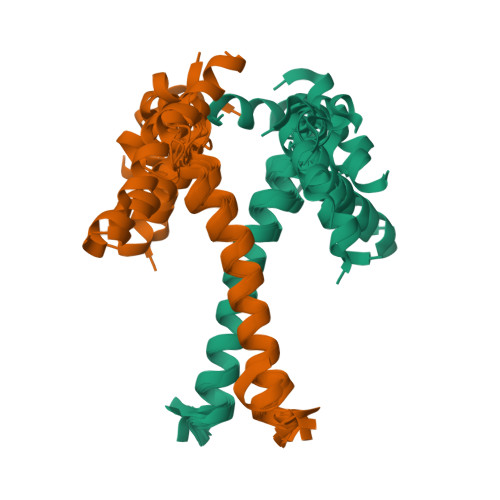
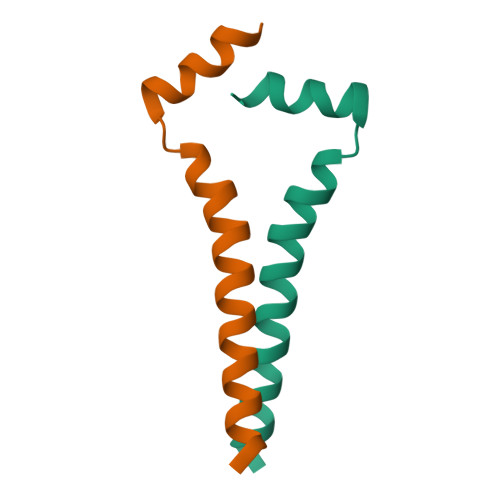
Dimeric structure of transmembrane domain of amyloid precursor protein in micellar environment.
Nadezhdin, K.D., Bocharova, O.V., Bocharov, E.V., Arseniev, A.S.(2012) FEBS Lett 586: 1687-1692
- PubMed: 22584060
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.04.062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LOH - PubMed Abstract:
Some pathogenic mutations associated with Alzheimer's disease are thought to affect structural-dynamic properties and the lateral dimerization of amyloid precursor protein (APP) in neuron membrane. Dimeric structure of APP transmembrane fragment Gln(686)-Lys(726) was determined in membrane-mimicking dodecylphosphocholine micelles using high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. The APP membrane-spanning α-helix Lys(699)-Lys(724) self-associates in a left-handed parallel dimer through extended heptad repeat motif I(702)X(3)M(706)X(2)G(709)X(3)A(713)X(2)I(716)X(3)I(720)X(2)I(723), whereas the juxtamembrane region Gln(686)-Val(695) constitutes the nascent helix, also sensing the dimerization. The dimerization mechanism of APP transmembrane domain has been described at atomic resolution for the first time and is important for understanding molecular events of APP sequential proteolytical cleavage resulting in amyloid-β peptide.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS, Str. Miklukho-Maklaya 16/10, Moscow 117997, Russian Federation.