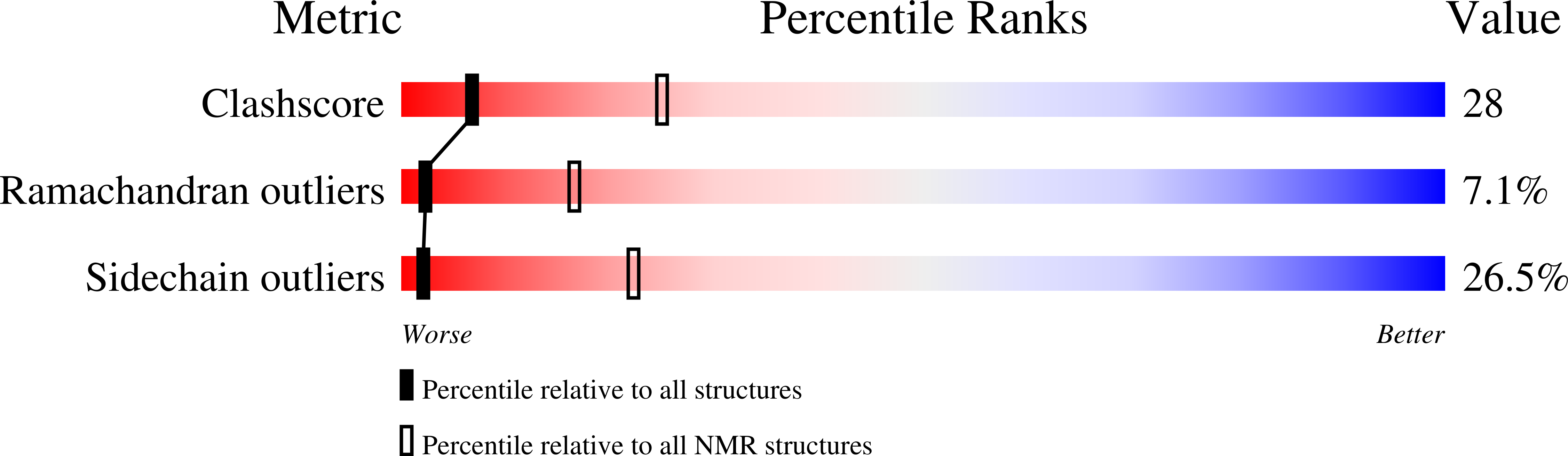NMR-assignments of a cytosolic domain of the C-terminus of polycystin-2
Schumann, F.H., Hoffmeister, H., Schmidt, M., Bader, R., Besl, E., Witzgall, R., Kalbitzer, H.R.(2009) Biomol NMR Assign 3: 141-144
- PubMed: 19636966
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9160-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
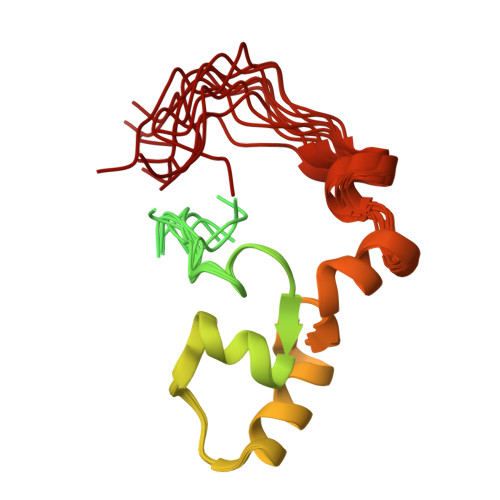
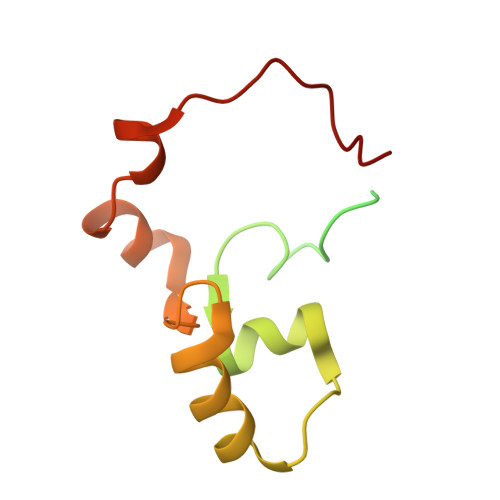
2KLD, 2KLE - PubMed Abstract:
Mutations in the PKD2 gene lead to the development of polycystic kidney disease (PKD). The PKD2 gene codes for polycystin-2, a cation channel with unknown function. The cytoplasmic, C-terminal domain interacts with a large number of proteins including mDia1, alpha-actinin, PIGEA-14, troponin, and tropomyosin. The C-terminal fragment polycystin-2 (680-796) consisting of 117 amino acids contains a putative calcium binding EF-hand. It was produced in Escherichia coli and enriched uniformly with (13)C and (15)N. The backbone and side chain resonances were assigned by multidimensional NMR methods, the obtained chemical shifts are typical for a partially folded protein. The chemical shifts obtained are in line with the existence of two paired helix-loop-helix (HLH) motifs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biophysics and Physical Biochemistry, University of Regensburg, 93040, Regensburg, Germany.