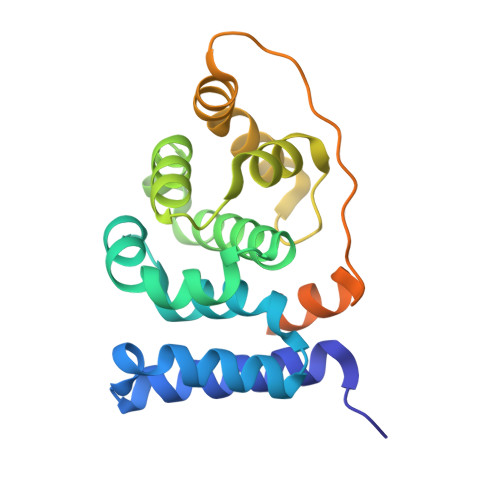
The Crystal Structure of the Carboxy-Terminal Domain of Human Translation Initiation Factor Eif5.
Bieniossek, C., Schutz, P., Bumann, M., Limacher, A., Uson, I., Baumann, U.(2006) J Mol Biology 360: 457
- PubMed: 16781736
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IU1 - PubMed Abstract:
The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of eukaryotic initiation factor 5 (eIF5) plays a central role in the formation of the multifactor complex (MFC), an important intermediate for the 43 S pre-initiation complex assembly. The IF5-CTD interacts directly with the translation initiation factors eIF1, eIF2-beta, and eIF3c, thus forming together with eIF2 bound Met-tRNA(i)(Met) the MFC. In this work we present the high resolution crystal structure of eIF5-CTD. This domain of the protein is exclusively composed out of alpha-helices and is homologous to the carboxy-terminal domain of eIF2B-epsilon (eIF2Bepsilon-CTD). The most striking difference in the two structures is an additional carboxy-terminal helix in eIF5. The binding sites of eIF2-beta, eIF3 and eIF1 were mapped onto the structure. eIF2-beta and eIF3 bind to non-overlapping patches of negative and positive electrostatic potential, respectively.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departement für Chemie und Biochemie, Universität Bern, Freiestrasse 3, CH-3012 Bern, Switzerland.