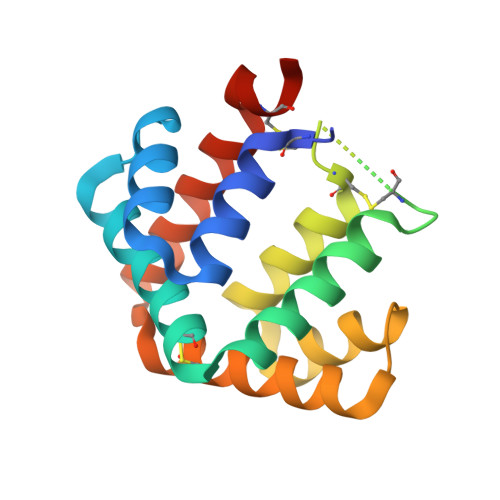
The crystal structure of the major cat allergen Fel d 1, a member of the secretoglobin family.
Kaiser, L., Gronlund, H., Sandalova, T., Ljunggren, H.G., van Hage-Hamsten, M., Achour, A., Schneider, G.(2003) J Biological Chem 278: 37730-37735
- PubMed: 12851385
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304740200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PUO - PubMed Abstract:
The domestic cat (Felis domesticus) is one of the most important causes of allergic asthma worldwide. The dominating cat allergen, Fel d 1, is composed of two heterodimers. Recently, it has been shown that recombinant Fel d 1, consisting of chain 2 and chain 1 fused together without additional linker, has immunological properties indistinguishable from the natural heterodimeric protein. Herein, we report the crystal structure of recombinant monomeric Fel d 1 at 1.85-A resolution, determined by multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction using selenomethionine substituted protein. Fel d 1 is an all-helical protein and consists of eight helices. The two halves of the recombinant Fel d 1 molecule, corresponding to the wild-type Fel d 1 chains, are very similar in three-dimensional structure, despite the lack of significant sequence identity. The structure of the Fel d 1 presents a striking similarity to that of uteroglobin, a steroid-inducible cytokine-like molecule with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. An internal, asymmetric cavity is formed in the Fel d 1 that could bind an endogenous ligand. The distribution of residues lining this cavity suggests that such a ligand must be amphipathic. The structure of Fel d 1 displays the localization of three previously defined Fel d 1 IgE epitopes on the surface of the protein. The three-dimensional structure provides a framework for rational design of hypoallergenic mutants aimed for treatment of cat allergy.
- Department of Medicine, Unit of Clinical Immunology and Allergy, Karolinska Institutet and Hospital L2:04, S-171 76 Stockholm, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: