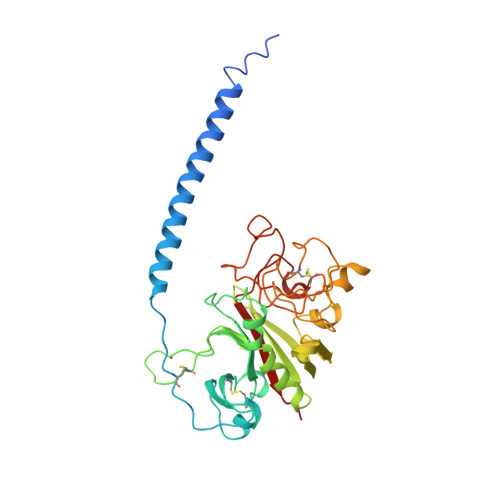
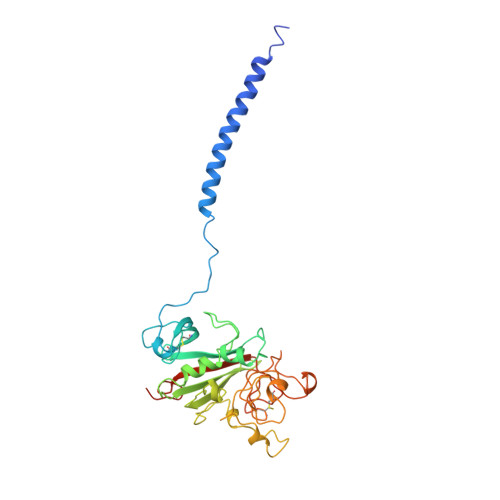
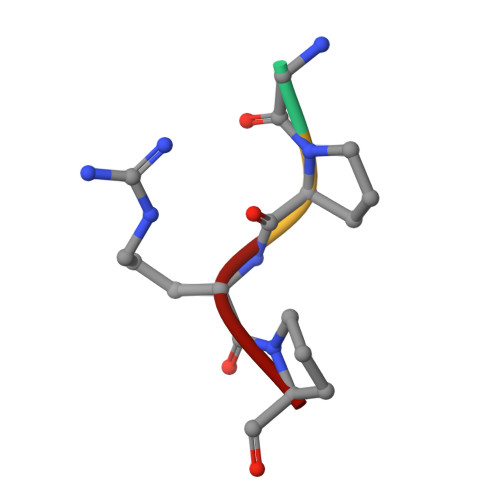
Crystal structure of fragment double-D from human fibrin with two different bound ligands.
Everse, S.J., Spraggon, G., Veerapandian, L., Riley, M., Doolittle, R.F.(1998) Biochemistry 37: 8637-8642
- PubMed: 9628725
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9804129
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FZC - PubMed Abstract:
Factor XIII-cross-linked fragment D (double-D) from human fibrin was crystallized in the presence of two different peptide ligands and the X-ray structure determined at 2.3 A. The peptide Gly-Pro-Arg-Pro-amide, which is an analogue of the knob exposed by the thrombin-catalyzed removal of fibrinopeptide A, was found to reside in the gamma-chain holes, and the peptide Gly-His-Arg-Pro-amide, which corresponds to the beta-chain knob, was found in the homologous beta-chain holes. The structure shows for the first time that the beta-chain knob does indeed bind to a homologous hole on the beta-chain. The gamma- and beta-chain holes are structurally very similar, and it is remarkable they are able to distinguish between these two peptides that differ by a single amino acid. Additionally, we have found that the beta-chain domain, like its gamma-chain counterpart, binds calcium.
- Center for Molecular Genetics, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, California 92093-0634, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: