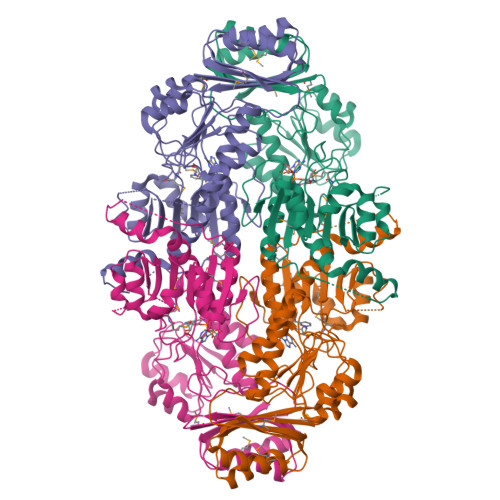
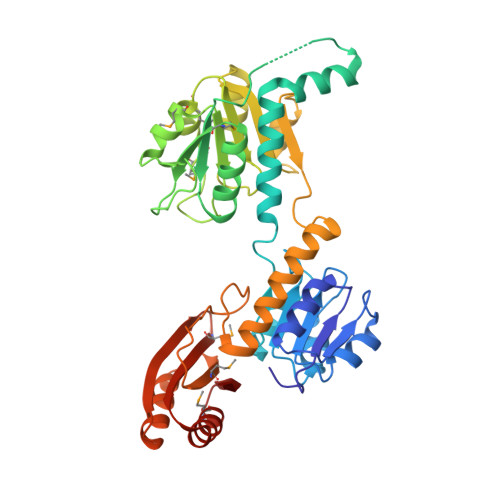
Multiconformational states in phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase
Bell, J.K., Grant, G.A., Banaszak, L.J.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 3450-3458
- PubMed: 15035616
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi035462e
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SC6 - PubMed Abstract:
Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PGDH) catalyzes the first step in the serine biosynthetic pathway. In lower plants and bacteria, the PGDH reaction is regulated by the end-product of the pathway, serine. The regulation occurs through a V(max) mechanism with serine binding and inhibition occurring in a cooperative manner. The three-dimensional structure of the serine inhibited enzyme, determined by previous work, showed a tetrameric enzyme with 222 symmetry and an unusual overall toroidal appearance. To characterize the allosteric, cooperative effects of serine, we identified W139G PGDH as an enzymatically active mutant responsive to serine but not in a cooperative manner. The position of W139 near a subunit interface and the active site cleft suggested that this residue is a key player in relaying allosteric effects. The 2.09 A crystal structure of W139G-PGDH, determined in the absence of serine, revealed major quaternary and tertiary structural changes. Contrary to the wildtype enzyme where residues encompassing residue 139 formed extensive intersubunit contacts, the corresponding residues in the mutant were conformationally flexible. Within each of the three-domain subunits, one domain has rotated approximately 42 degrees relative to the other two. The resulting quaternary structure is now in a novel conformation creating new subunit-to-subunit contacts and illustrates the unusual flexibility in this V(max) regulated enzyme. Although changes at the regulatory domain interface have implications in other enzymes containing a similar regulatory or ACT domain, the serine binding site in W139G PGDH is essentially unchanged from the wildtype enzyme. The structural and previous biochemical characterization of W139G PGDH suggests that the allosteric regulation of PGDH is mediated not only by changes occurring at the ACT domain interface but also by conformational changes at the interface encompassing residue W139.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55455, USA.