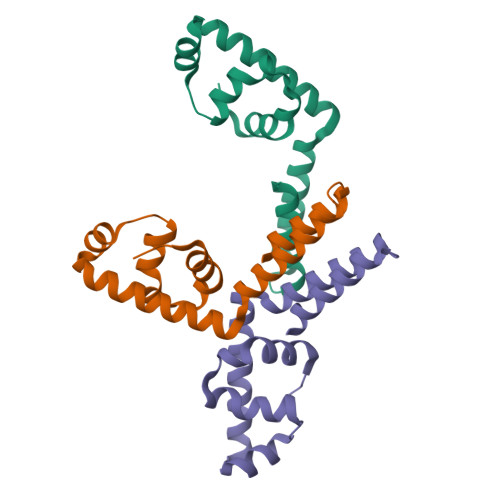
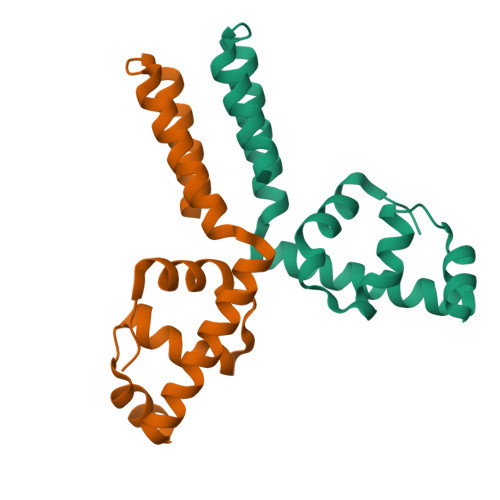
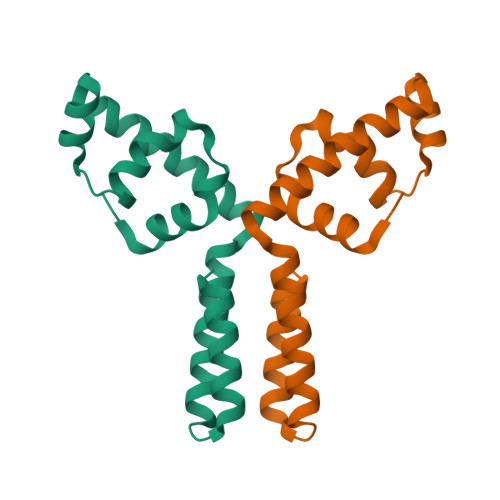
Structure of the putative DNA-binding protein SP_1288 from Streptococcus pyogenes.
Oganesyan, V., Pufan, R., DeGiovanni, A., Yokota, H., Kim, R., Kim, S.H.(2004) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60: 1266-1271
- PubMed: 15213388
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444904009394
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1S7O - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the putative DNA-binding protein SP_1288 (gi/15675166, also listed as gi/28895954) from Streptococcus pyogenes has been determined by X-ray crystallography to a resolution of 2.3 A using anomalous diffraction data at the Se peak wavelength. SP_1288 belongs to a family of proteins whose cellular function is associated with the signal recognition particle; no structural information has been available until now about the members of the family. Crystallographic analysis revealed that the overall fold of SP_1288 consists exclusively of alpha-helices and that 75% of the structure has good similarity to domain 4 of the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. This suggests its possible involvement in the biochemical function of transcription initiation, which includes interaction with DNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, Physical Biosciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720, USA.