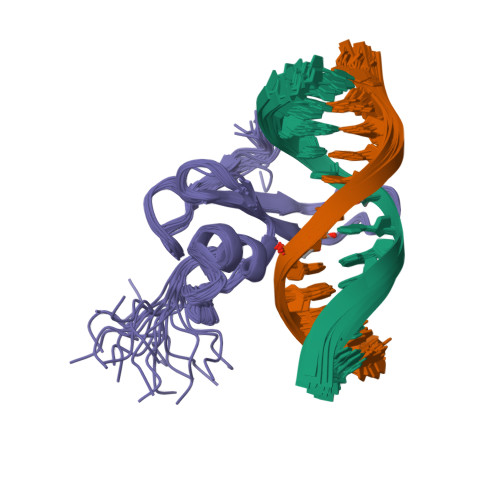
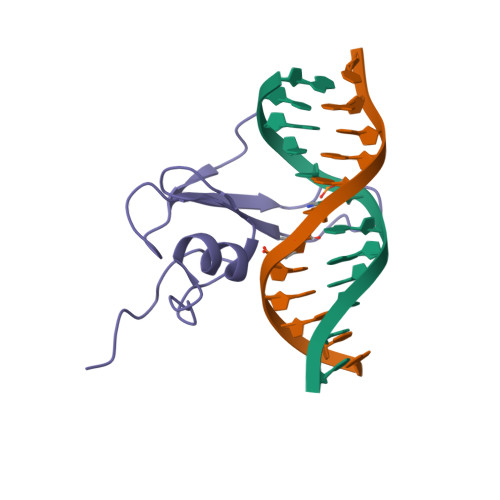
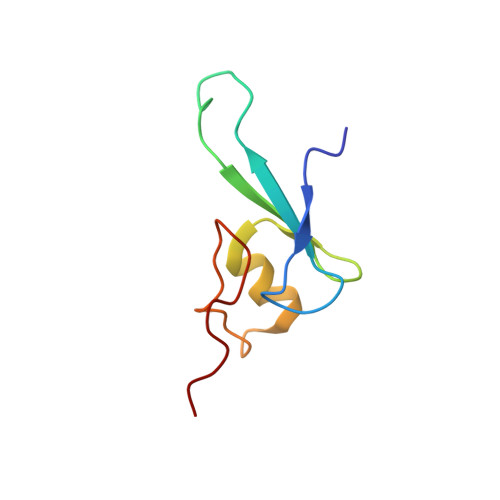
Solution structure of the methyl-CpG binding domain of human MBD1 in complex with methylated DNA.
Ohki, I., Shimotake, N., Fujita, N., Jee, J., Ikegami, T., Nakao, M., Shirakawa, M.(2001) Cell 105: 487-497
- PubMed: 11371345
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00324-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IG4 - PubMed Abstract:
In vertebrates, the biological consequences of DNA methylation are often mediated by protein factors containing conserved methyl-CpG binding domains (MBDs). Mutations in the MBD protein MeCP2 cause the neurodevelopmental disease Rett syndrome. We report here the solution structure of the MBD of the human methylation-dependent transcriptional regulator MBD1 bound to methylated DNA. DNA binding causes a loop in MBD1 to fold into a major and novel DNA binding interface. Recognition of the methyl groups and CG sequence at the methylation site is due to five highly conserved residues that form a hydrophobic patch. The structure indicates how MBD may access nucleosomal DNA without encountering steric interference from core histones, and provides a basis to interpret mutations linked to Rett syndrome in MeCP2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Biological Sciences, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma, 630-0101, Nara, Japan.