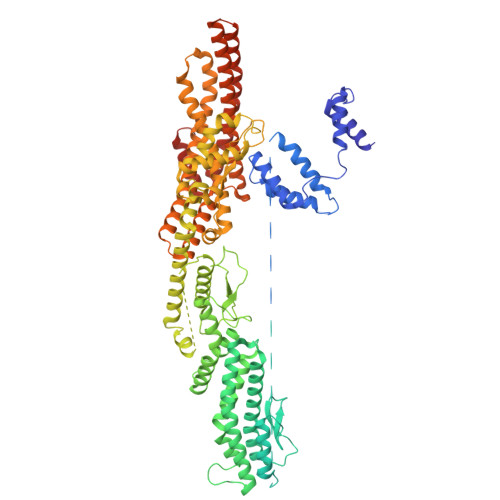
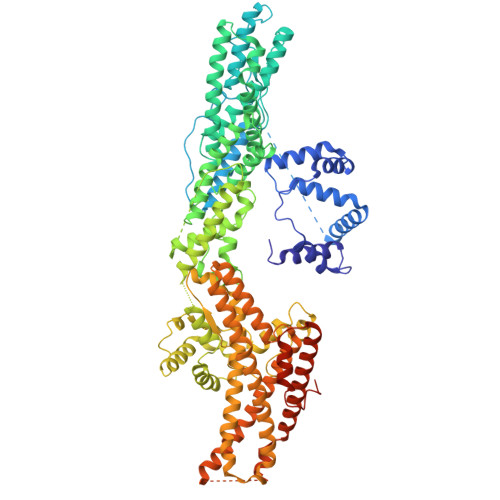
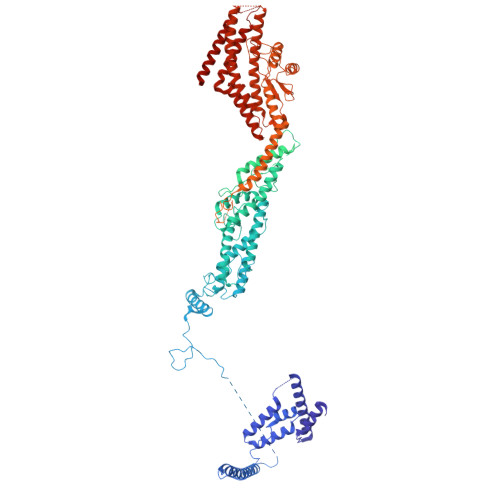
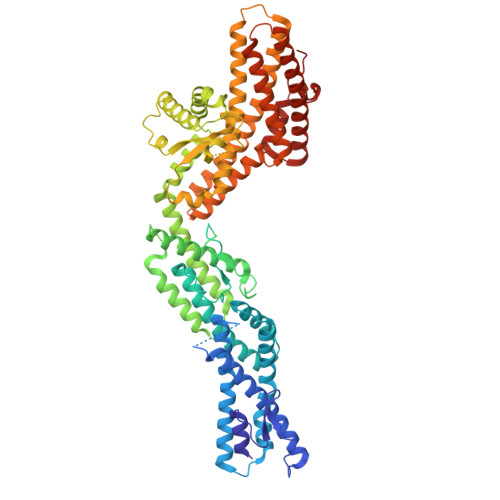
Partial closure of the gamma-tubulin ring complex by CDK5RAP2 activates microtubule nucleation.
Xu, Y., Munoz-Hernandez, H., Krutyholowa, R., Marxer, F., Cetin, F., Wieczorek, M.(2024) Dev Cell 59: 3161
- PubMed: 39321808
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2024.09.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9G3X, 9G3Y, 9G3Z, 9G40 - PubMed Abstract:
Microtubule nucleation is templated by the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC), but its structure deviates from the geometry of α-/β-tubulin in the microtubule, explaining the complex's poor nucleating activity. Several proteins may activate the γ-TuRC, but the mechanisms underlying activation are not known. Here, we determined the structure of the porcine γ-TuRC purified using CDK5RAP2's centrosomin motif 1 (CM1). We identified an unexpected conformation of the γ-TuRC bound to multiple protein modules containing MZT2, GCP2, and CDK5RAP2, resulting in a long-range constriction of the γ-tubulin ring that brings it in closer agreement with the 13-protofilament microtubule. Additional CDK5RAP2 promoted γ-TuRC decoration and stimulated the microtubule-nucleating activities of the porcine γ-TuRC and a reconstituted, CM1-free human complex in single-molecule assays. Our results provide a structural mechanism for the control of microtubule nucleation by CM1 proteins and identify conformational transitions in the γ-TuRC that prime it for microtubule nucleation.
- Department of Biology, Institute of Molecular Biology and Biophysics, ETH Zürich, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: