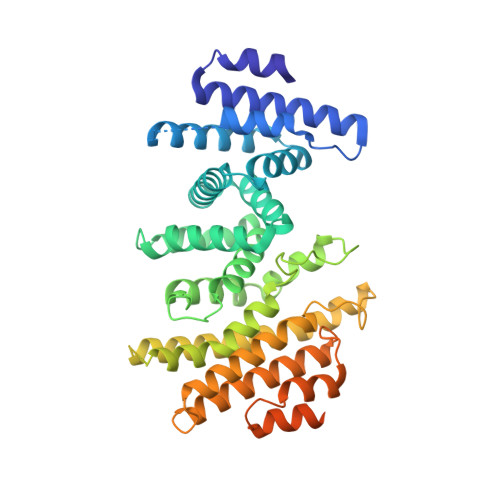
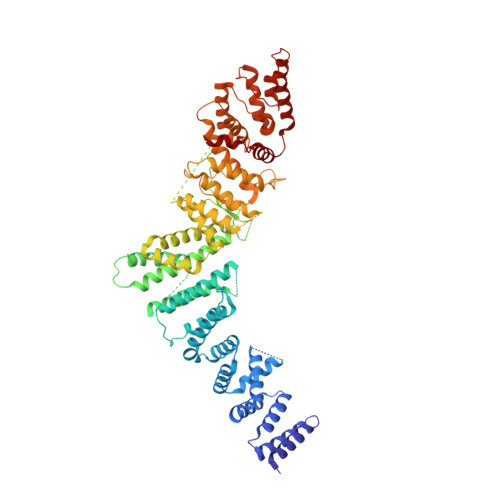
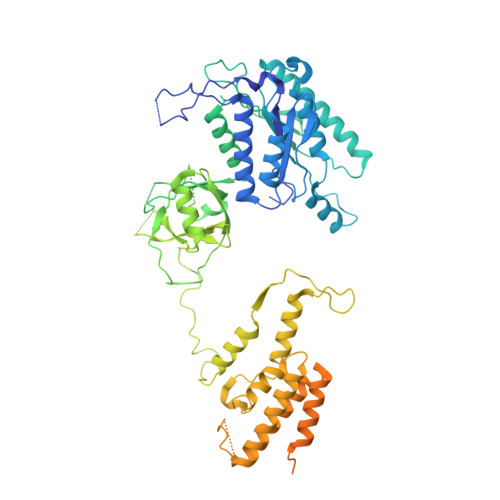
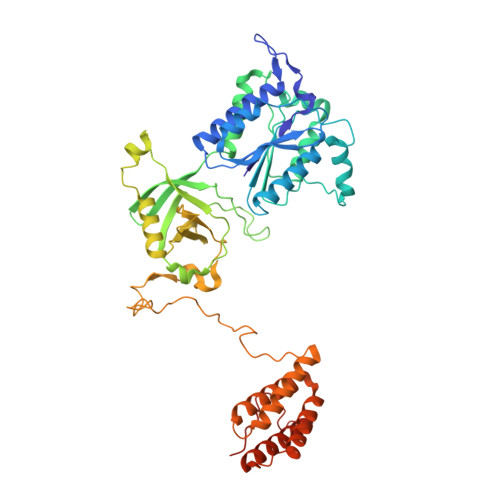
Structural basis of the Integrator complex assembly and association with transcription factors.
Razew, M., Fraudeau, A., Pfleiderer, M.M., Linares, R., Galej, W.P.(2024) Mol Cell 84: 2542
- PubMed: 38823386
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2024.05.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9EOC, 9EOF, 9EP1, 9EP4, 9FA4, 9FA7 - PubMed Abstract:
Integrator is a multi-subunit protein complex responsible for premature transcription termination of coding and non-coding RNAs. This is achieved via two enzymatic activities, RNA endonuclease and protein phosphatase, acting on the promoter-proximally paused RNA polymerase Ⅱ (RNAPⅡ). Yet, it remains unclear how Integrator assembly and recruitment are regulated and what the functions of many of its core subunits are. Here, we report the structures of two human Integrator sub-complexes: INTS10/13/14/15 and INTS5/8/10/15, and an integrative model of the fully assembled Integrator bound to the RNAPⅡ paused elongating complex (PEC). An in silico protein-protein interaction screen of over 1,500 human transcription factors (TFs) identified ZNF655 as a direct interacting partner of INTS13 within the fully assembled Integrator. We propose a model wherein INTS13 acts as a platform for the recruitment of TFs that could modulate the stability of the Integrator's association at specific loci and regulate transcription attenuation of the target genes.
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory, EMBL Grenoble, 71 Avenue des Martyrs, 38042 Grenoble, France.
Organizational Affiliation: