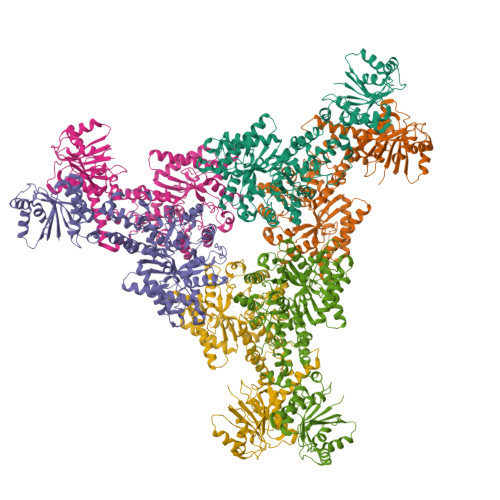
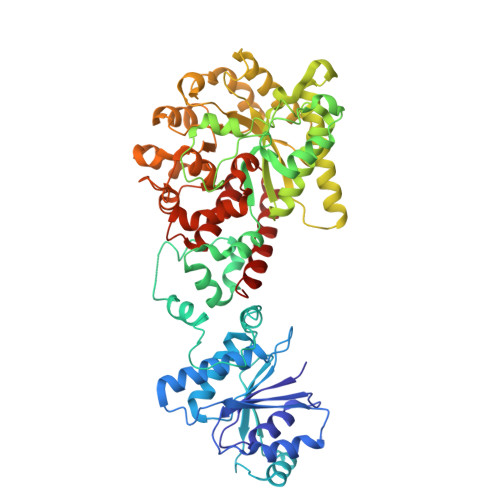
The CRISPR-associated adenosine deaminase Cad1 converts ATP to ITP to provide antiviral immunity.
Baca, C.F., Majumder, P., Hickling, J.H., Ye, L., Teplova, M., Brady, S.F., Patel, D.J., Marraffini, L.A.(2024) Cell 187: 7183
- PubMed: 39471810
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9C67, 9C68, 9C69, 9C6A, 9C6C, 9C6F, 9C77, 9CDB - PubMed Abstract:
Type III CRISPR systems provide immunity against genetic invaders through the production of cyclic oligo-adenylate (cA n ) molecules that activate effector proteins that contain CRISPR-associated Rossman fold (CARF) domains. Here, we characterized the function and structure of an effector in which the CARF domain is fused to an adenosine deaminase domain, CRISPR-associated adenosine deaminase 1 (Cad1). We show that upon binding of cA 4 or cA 6 to its CARF domain, Cad1 converts ATP to ITP, both in vivo and in vitro. Cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structural studies on full-length Cad1 reveal an hexameric assembly composed of a trimer of dimers, with bound ATP at inter-domain sites required for activity and ATP/ITP within deaminase active sites. Upon synthesis of cA n during phage infection, Cad1 activation leads to a growth arrest of the host that prevents viral propagation. Our findings reveal that CRISPR-Cas systems employ a wide range of molecular mechanisms beyond nucleic acid degradation to provide adaptive immunity in prokaryotes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Bacteriology, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065, USA; Tri-Institutional PhD Program in Chemical Biology, Weill Cornell Medical College, Rockefeller University and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065, USA.