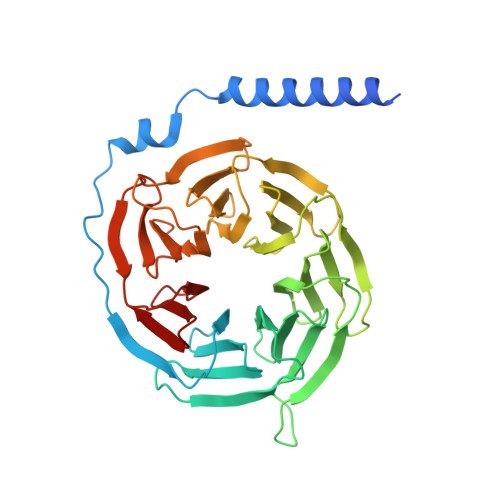
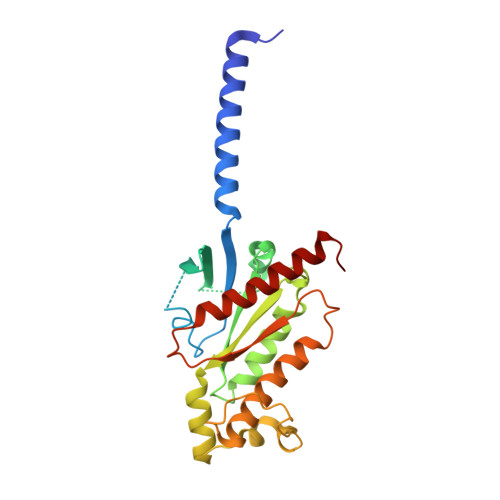
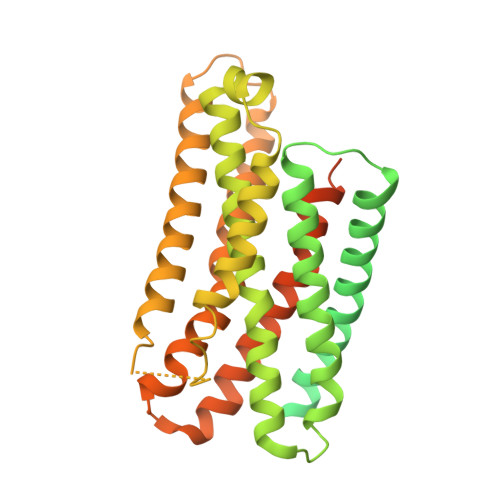
MRGPRX4 mediates phospho-drug-associated pruritus in a humanized mouse model.
Chien, D.C., Limjunyawong, N., Cao, C., Meixiong, J., Peng, Q., Ho, C.Y., Fay, J.F., Roth, B.L., Dong, X.(2024) Sci Transl Med 16: eadk8198-eadk8198
- PubMed: 38718132
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.adk8198
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YRG - PubMed Abstract:
The phosphate modification of drugs is a common chemical strategy to increase solubility and allow for parenteral administration. Unfortunately, phosphate modifications often elicit treatment- or dose-limiting pruritus through an unknown mechanism. Using unbiased high-throughput drug screens, we identified the Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor X4 (MRGPRX4), a primate-specific, sensory neuron receptor previously implicated in itch, as a potential target for phosphate-modified compounds. Using both G q -mediated calcium mobilization and G protein-independent GPCR assays, we found that phosphate-modified compounds potently activate MRGPRX4. Furthermore, a humanized mouse model expressing MRGPRX4 in sensory neurons exhibited robust phosphomonoester prodrug-evoked itch. To characterize and confirm this interaction, we further determined the structure of MRGPRX4 in complex with a phosphate-modified drug through single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and identified critical amino acid residues responsible for the binding of the phosphate group. Together, these findings explain how phosphorylated drugs can elicit treatment-limiting itch and identify MRGPRX4 as a potential therapeutic target to suppress itch and to guide future drug design.
- Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: