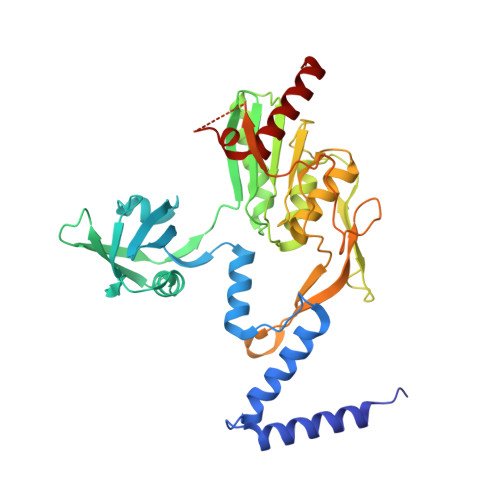
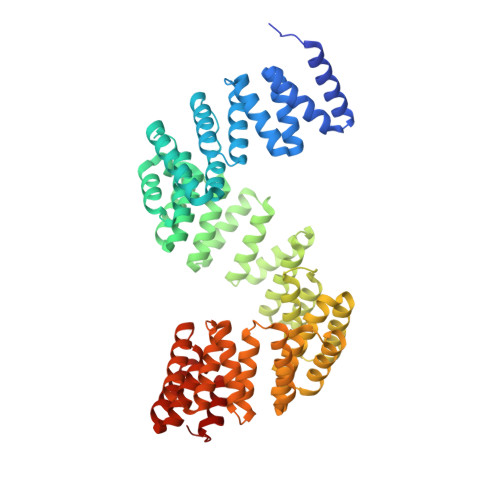
P. aeruginosa CtpA protease adopts a novel activation mechanism to initiate the proteolytic process.
Hsu, H.C., Wang, M., Kovach, A., Darwin, A.J., Li, H.(2024) EMBO J 43: 1634-1652
- PubMed: 38467832
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-024-00069-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SXE, 8SXF, 8SXG, 8SXH - PubMed Abstract:
During bacterial cell growth, hydrolases cleave peptide cross-links between strands of the peptidoglycan sacculus to allow new strand insertion. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa carboxyl-terminal processing protease (CTP) CtpA regulates some of these hydrolases by degrading them. CtpA assembles as an inactive hexamer composed of a trimer-of-dimers, but its lipoprotein binding partner LbcA activates CtpA by an unknown mechanism. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of the CtpA-LbcA complex. LbcA has an N-terminal adaptor domain that binds to CtpA, and a C-terminal superhelical tetratricopeptide repeat domain. One LbcA molecule attaches to each of the three vertices of a CtpA hexamer. LbcA triggers relocation of the CtpA PDZ domain, remodeling of the substrate binding pocket, and realignment of the catalytic residues. Surprisingly, only one CtpA molecule in a CtpA dimer is activated upon LbcA binding. Also, a long loop from one CtpA dimer inserts into a neighboring dimer to facilitate the proteolytic activity. This work has revealed an activation mechanism for a bacterial CTP that is strikingly different from other CTPs that have been characterized structurally.
- Department of Structural Biology, Van Andel Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: