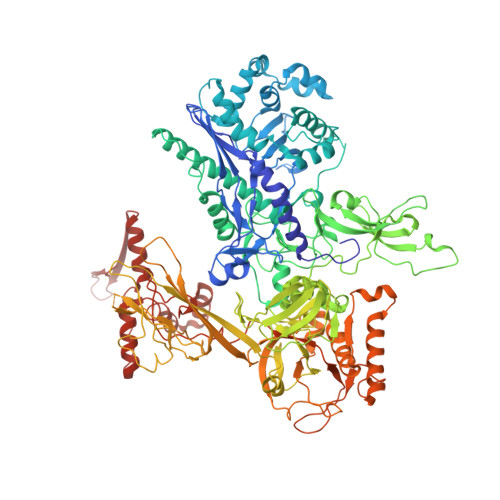
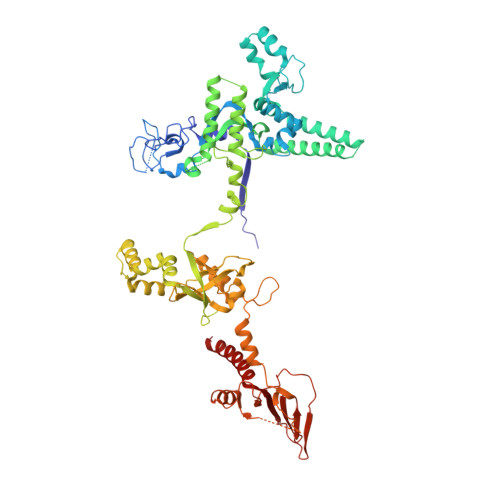
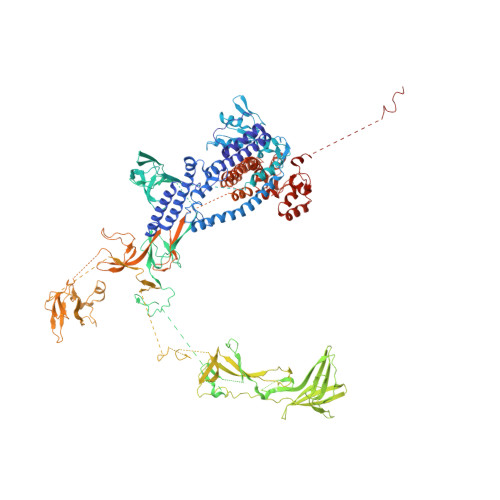
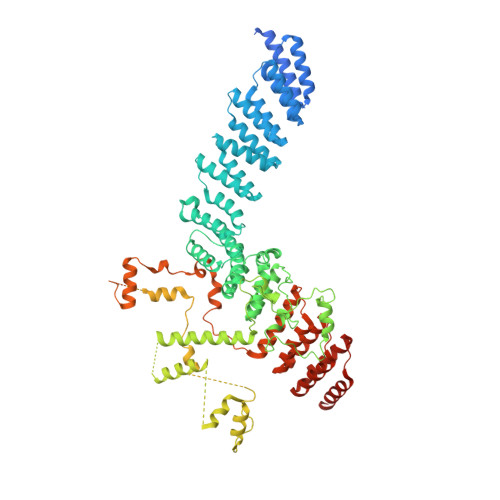
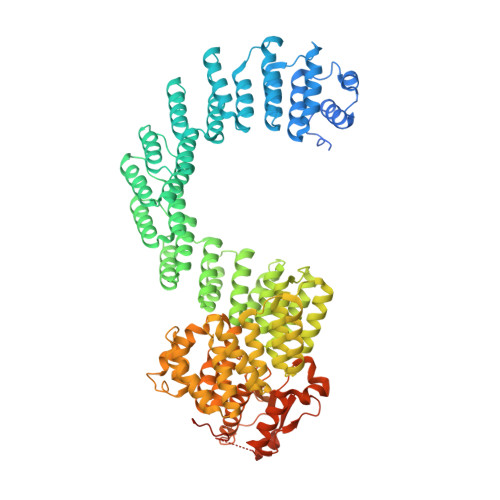
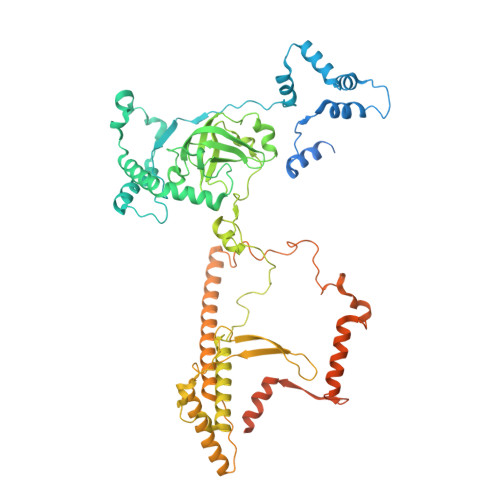
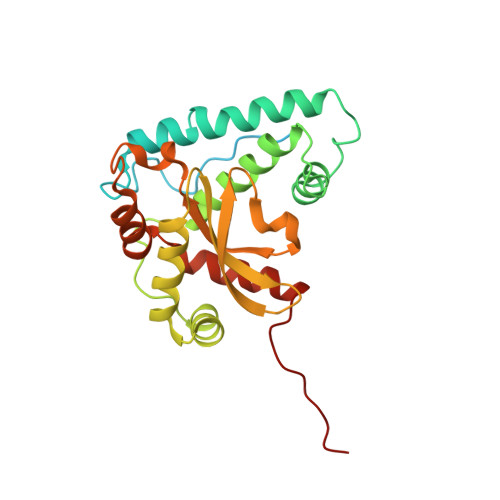
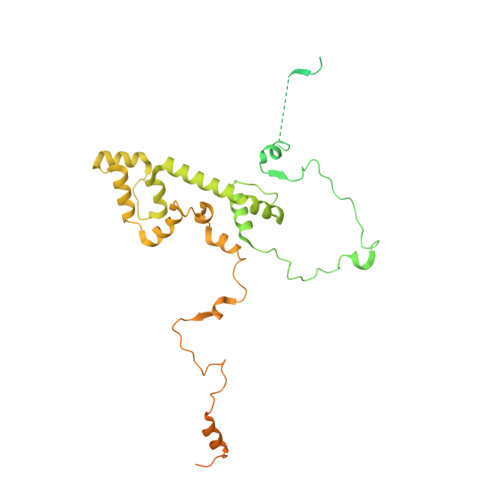
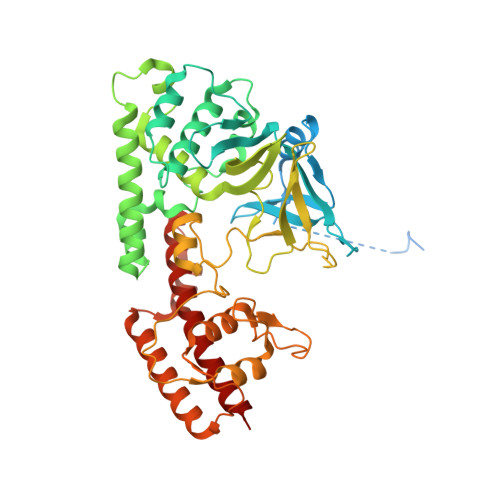
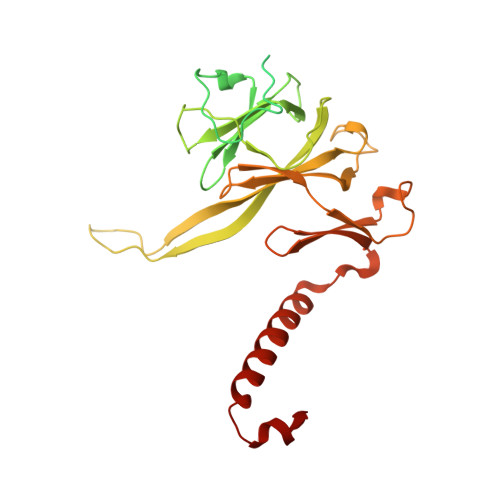
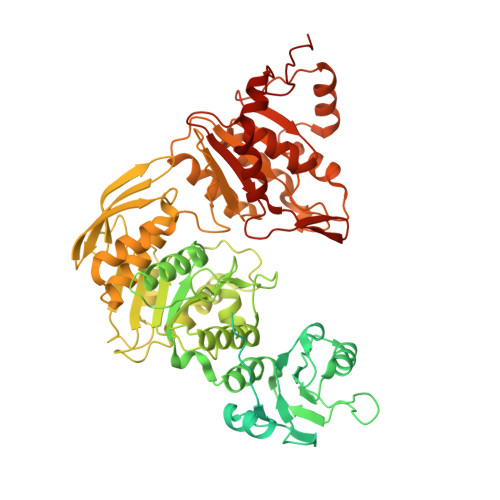
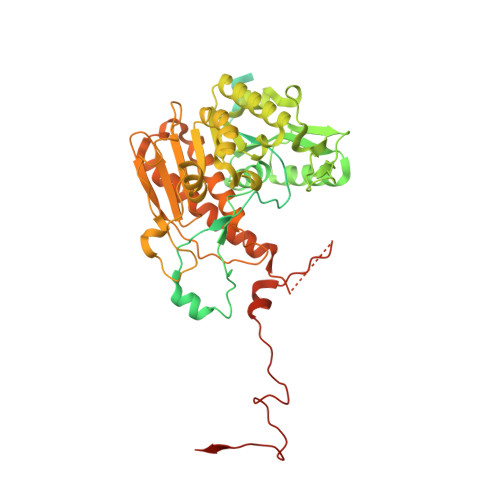
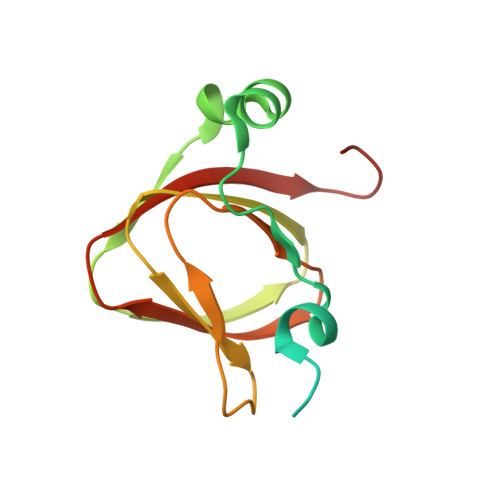
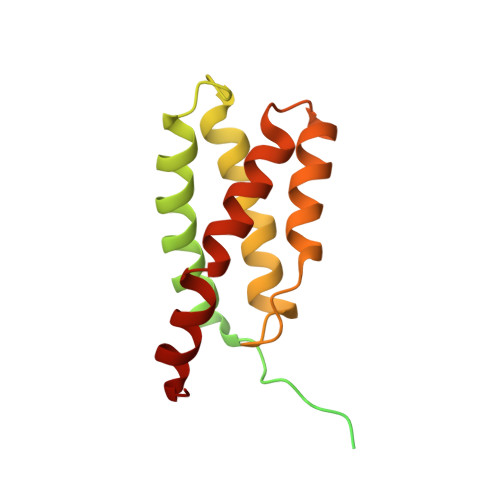
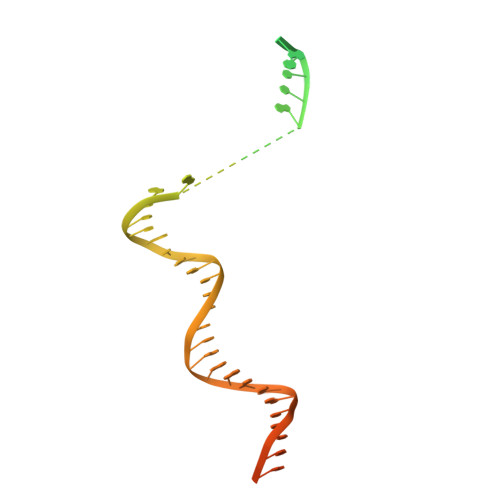
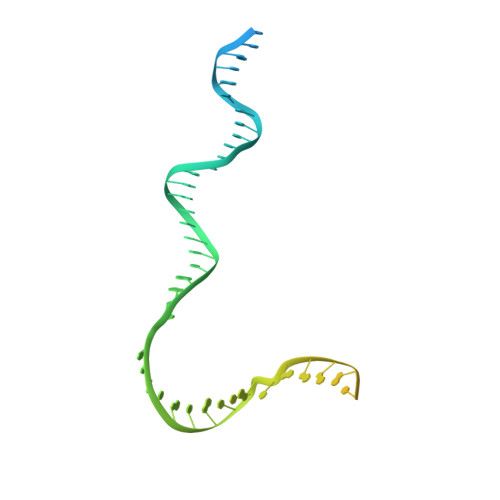
Structure of the plant plastid-encoded RNA polymerase.
Vergara-Cruces, A., Pramanick, I., Pearce, D., Vogirala, V.K., Byrne, M.J., Low, J.K.K., Webster, M.W.(2024) Cell 187: 1145-1159.e21
- PubMed: 38428394
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8R5O, 8R6S, 8RAS, 8RDJ - PubMed Abstract:
Chloroplast genes encoding photosynthesis-associated proteins are predominantly transcribed by the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP). PEP is a multi-subunit complex composed of plastid-encoded subunits similar to bacterial RNA polymerases (RNAPs) stably bound to a set of nuclear-encoded PEP-associated proteins (PAPs). PAPs are essential to PEP activity and chloroplast biogenesis, but their roles are poorly defined. Here, we present cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of native 21-subunit PEP and a PEP transcription elongation complex from white mustard (Sinapis alba). We identify that PAPs encase the core polymerase, forming extensive interactions that likely promote complex assembly and stability. During elongation, PAPs interact with DNA downstream of the transcription bubble and with the nascent mRNA. The models reveal details of the superoxide dismutase, lysine methyltransferase, thioredoxin, and amino acid ligase enzymes that are subunits of PEP. Collectively, these data provide a foundation for the mechanistic understanding of chloroplast transcription and its role in plant growth and adaptation.
- Department of Biochemistry and Metabolism, John Innes Centre, Norwich Research Park, Norwich, NR4 7UH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: