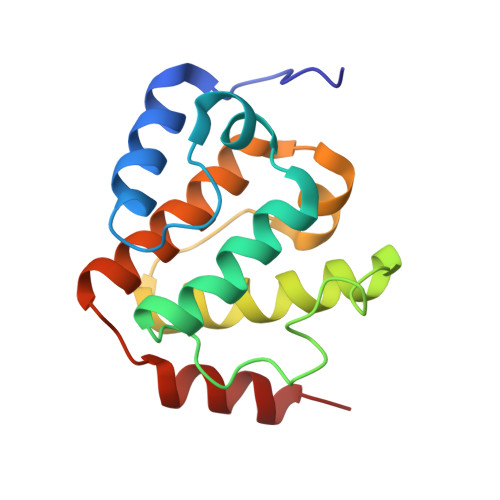
1 H, 13 C, and 15 N resonance assignments and solution structure of the N-terminal divergent calponin homology (NN-CH) domain of human intraflagellar transport protein 54.
Kuwasako, K., Dang, W., He, F., Takahashi, M., Tsuda, K., Nagata, T., Tanaka, A., Kobayashi, N., Kigawa, T., Guntert, P., Shirouzu, M., Yokoyama, S., Muto, Y.(2024) Biomol NMR Assign 18: 71-78
- PubMed: 38551798
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-024-10170-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8KCQ - PubMed Abstract:
The intraflagellar transport (IFT) machinery plays a crucial role in the bidirectional trafficking of components necessary for ciliary signaling, such as the Hedgehog, Wnt/PCR, and cAMP/PKA systems. Defects in some components of the IFT machinery cause dysfunction, leading to a wide range of human diseases and developmental disorders termed ciliopathies, such as nephronophthisis. The IFT machinery comprises three sub-complexes: BBsome, IFT-A, and IFT-B. The IFT protein 54 (IFT54) is an important component of the IFT-B sub-complex. In anterograde movement, IFT54 binds to active kinesin-II, walking along the cilia microtubule axoneme and carrying the dynein-2 complex in an inactive state, which works for retrograde movement. Several mutations in IFT54 are known to cause Senior-Loken syndrome, a ciliopathy. IFT54 possesses a divergent Calponin Homology (CH) domain termed as NN-CH domain at its N-terminus. However, several aspects of the function of the NN-CH domain of IFT54 are still obscure. Here, we report the 1 H, 15 N, and 13 C resonance assignments of the NN-CH domain of human IFT54 and its solution structure. The NN-CH domain of human IFT54 adopts essentially the α1-α2-α3-α4-α5 topology as that of mouse IFT54, whose structure was determined by X-ray crystallographic study. The structural information and assignments obtained in this study shed light on the molecular function of the NN-CH domain in IFT54.
- RIKEN, Systems and Structural Biology Center, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi, Yokohama, 230-0045, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: