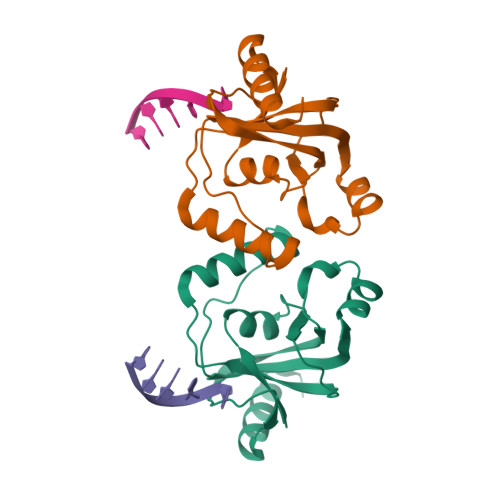
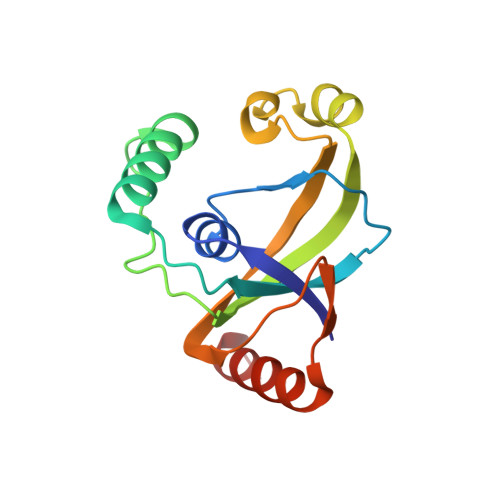
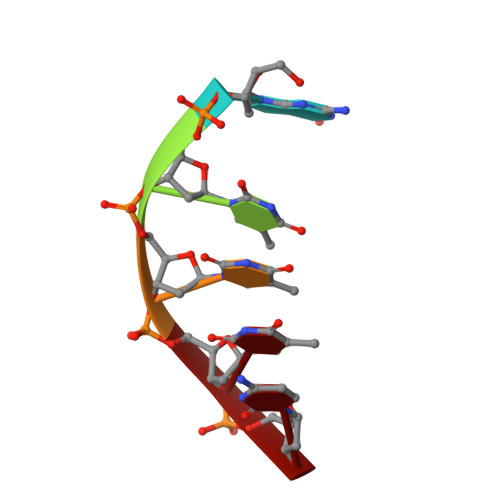
Biochemical and structural characterization of the DNA-binding properties of human TRIP4 ASCH domain reveals insights into its functional role.
Hu, C., Chen, Z., Wang, G., Yang, H., Ding, J.(2024) Structure 32: 1208
- PubMed: 38870938
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2024.05.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YEW, 8YEY, 8YFI, 8YFJ, 8YXW, 8YXX - PubMed Abstract:
TRIP4 is a conserved transcriptional coactivator that is involved in the regulation of the expression of multiple genes. It consists of a classical N-terminal C2HC5-like zinc-finger domain and a conserved C-terminal ASCH domain. Here, we characterized the DNA-binding properties of the human TRIP4 ASCH domain. Our biochemical data show that TRIP4-ASCH has comparable binding affinities toward ssDNA and dsDNA of different lengths, sequences, and structures. The crystal structures reveal that TRIP4-ASCH binds to DNA substrates in a sequence-independent manner through two adjacent positively charged surface patches: one binds to the 5'-end of DNA, and the other binds to the 3'-end of DNA. Further mutagenesis experiments and binding assays confirm the functional roles of key residues involved in DNA binding. In summary, our data demonstrate that TRIP4-ASCH binds to the 5' and 3'-ends of DNA in a sequence-independent manner, which will facilitate further studies of the biological function of TRIP4.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of RNA Innovation, Science and Engineering, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China; School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, 393 Middle Huaxia Road, Shanghai 201210, China.