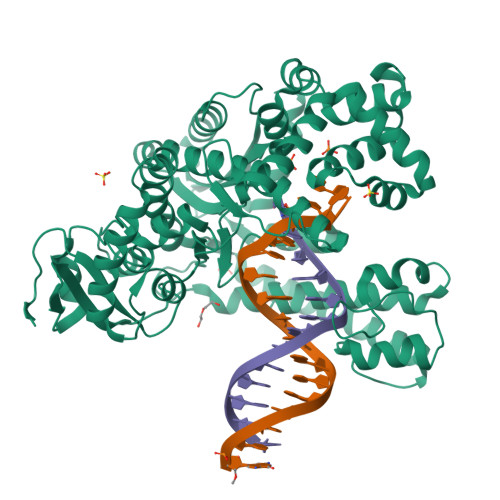
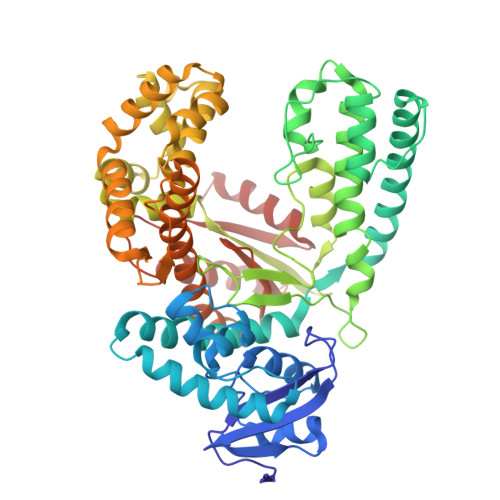
Structural Basis for C2'-methoxy Recognition by DNA Polymerases and Function Improvement.
Wen, C., Wang, G., Yang, L., Chen, T., Liu, H., Gong, W.(2024) J Mol Biology 436: 168744-168744
- PubMed: 39147125
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168744
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8XJR, 8XK7, 8XK9 - PubMed Abstract:
DNA modified with C2'-methoxy (C2'-OMe) greatly enhances its resistance to nucleases, which is beneficial for the half-life of aptamers and DNA nanomaterials. Although the unnatural DNA polymerases capable of incorporating C2'-OMe modified nucleoside monophosphates (C2'-OMe-NMPs) were engineered via directed evolution, the detailed molecular mechanism by which an evolved DNA polymerase recognizes C2'-OMe-NTPs remains poorly understood. Here, we present the crystal structures of the evolved Stoffel fragment of Taq DNA polymerase SFM4-3 processing the C2'-OMe-GTP in different states. Our results reveal the structural basis for recognition of C2'-methoxy by SFM4-3. Based on the analysis of other mutated residues in SFM4-3, a new Stoffel fragment variant with faster catalytic rate and stronger inhibitor-resistance was obtained. In addition, the capture of a novel pre-insertion co-existing with template 5'-overhang stacking conformation provides insight into the catalytic mechanism of Taq DNA polymerase.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biological Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230027, PR China.